It feels as though AI Mode snuck in the door behind AI Overviews as it was slowly rolled out, but according to Google, it’s the future of search, so we need to get to know it better.
Businesses and marketers want to be visible and are all scrambling to figure out the path forward with AI Mode. Your audience is going to be using AI search platforms whether they want to or not so your business needs to be present on them.
In their recent webinar packed with deep technical knowledge and a few reality checks for SEOs, Mike King (iPullRank) and Andrea Volpini (WordLift) made one thing clear: the SEO world isn’t ready for what’s coming next.
AI Mode is a whole new paradigm that demands a rethink of how we optimize for search, and Relevance Engineering will be what gets us where we need to go.
Let’s break down their discussion.
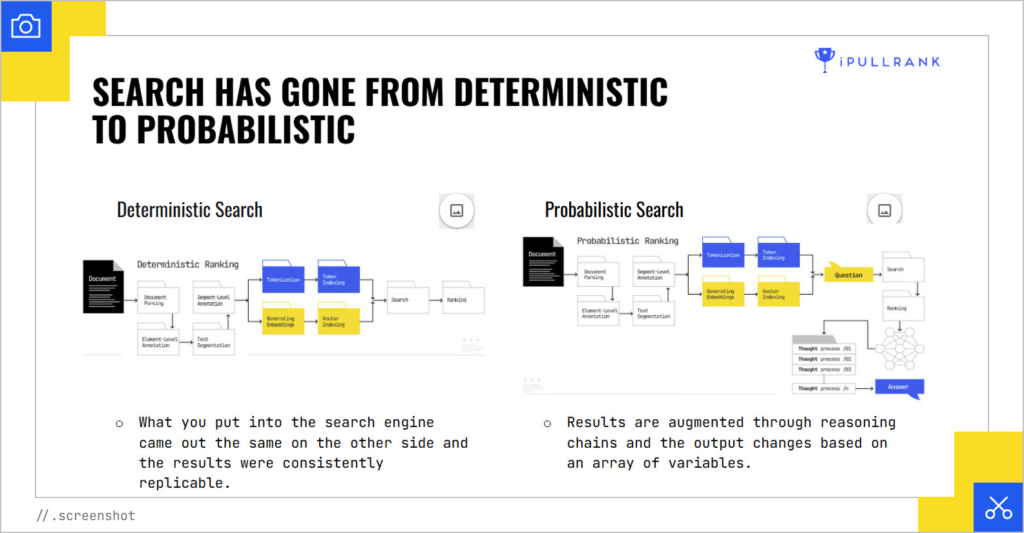
From Deterministic to Probabilistic Search
Mike kicked things off by explaining how AI Mode fundamentally changes how Google processes search. Historically, search was deterministic, where you would put in content and receive a predictable output. Now, it’s probabilistic:
- AI looks beyond the documents that directly rank for a keyword.
- It runs synthetic queries behind the scenes to pull together the most relevant passages.
- It puts the passages through reasoning steps.
- Then it generates a response that can be different each time.
That means your page is being assessed in ways you can’t always predict.
“The SEO community and industry is really not prepared for this moment.”
- Mike King
AI Mode and AI Overviews (AIOs) operate on the same principle. They use the query fan-out technique, which takes your core query and generates multiple variations, then runs them through a series of large language models (LLMs).
Initially, we didn’t know that AI Overviews were leveraging this Query Fan-Out technique. It explains why SEOs were confused when cited pages weren’t ranking in the top 100 for the original query.
Want to learn more about how AI Overviews’ performance has changed over the past couple of years? Read my meta-analysis of two years of AI Overview studies.
These LLMs are used for selecting information, generating a response, determining whether any creative media is needed, and making query recommendations. What’s that look like?
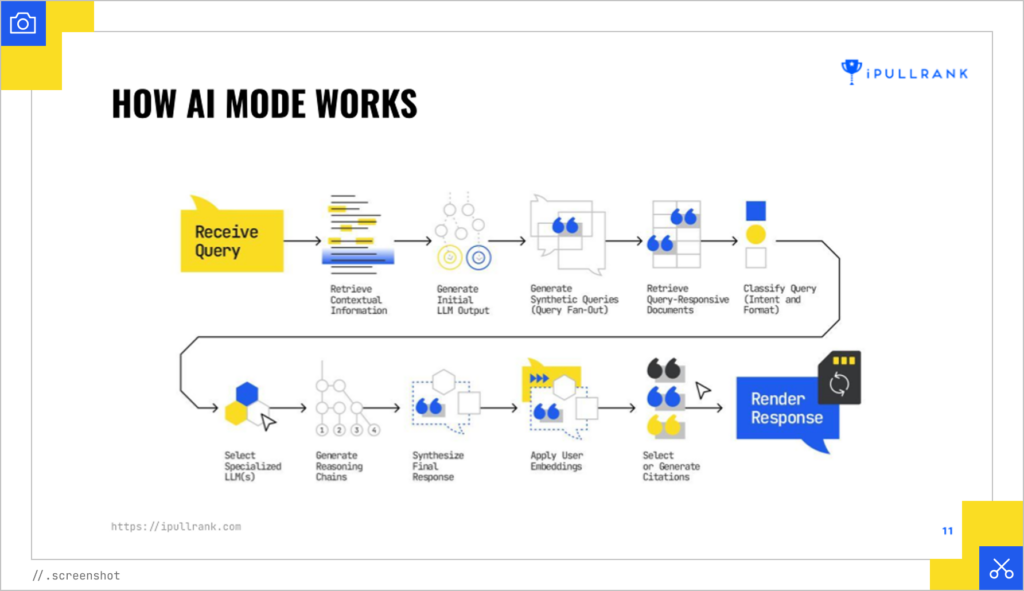
“The query fan-out technique…is the big thing that I think we need to be thinking about in our space.”
- Mike King
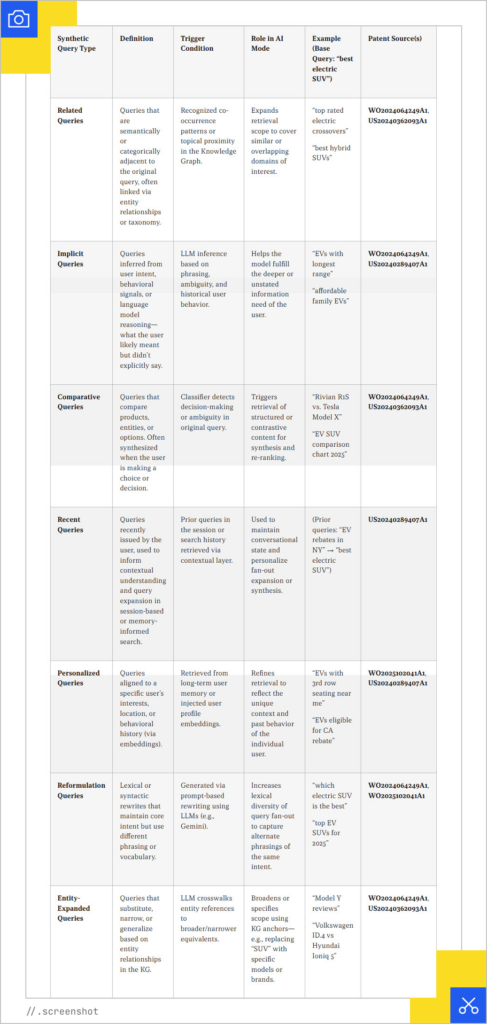
There are nine main types of queries, and the models classify the query, determine the best format for the answer, and decide whether to generate text, visuals, or other creative content:
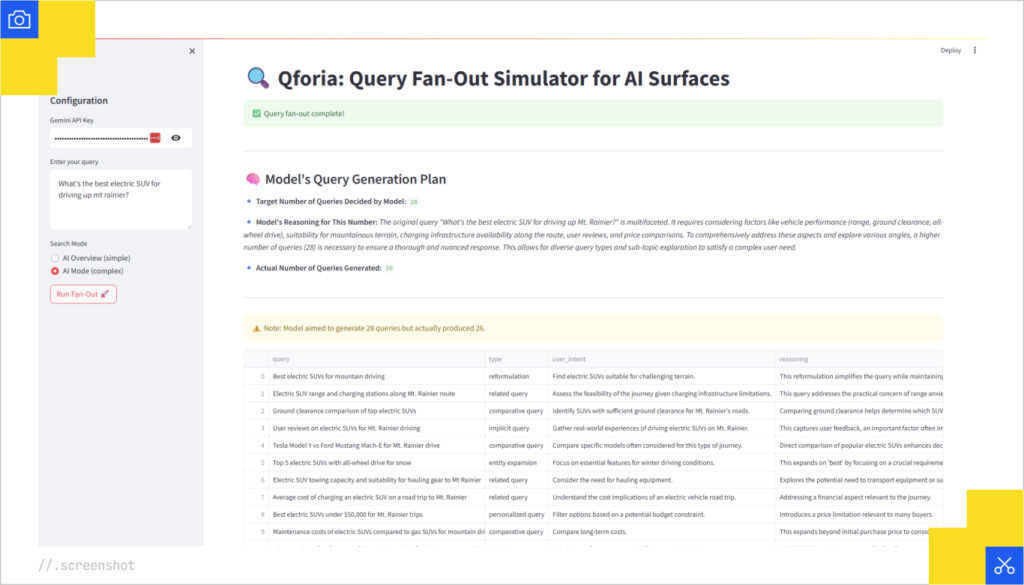
And if you’re wondering how to get a handle on all this, Mike developed Qforia, a tool that reverse-engineers the query by looking at citations, surfacing their rankings, and simulating how AI might generate synthetic queries. It’s still in early stages, but a solid starting point if you’re trying to see how Gemini (Google’s model) is thinking. Keep in mind, Google uses different versions of Gemini for Overviews vs. AI Mode.
Passages Over Pages
If you’re an analogy person like me, you’ll appreciate Mike’s description of AI search as a raffle. Much like having more raffle tickets gives you a better chance of winning the raffle, the more relevant passages you have, the better your chances of being surfaced in AI Mode.
LLMs have become hyper-personalized, taking info from across the Google ecosystem. This can include other pages you’ve looked at in your Chrome history, products you’ve bought, and even your Gmail. They generate vector embeddings for you and use them as a filter for your personalized query result.
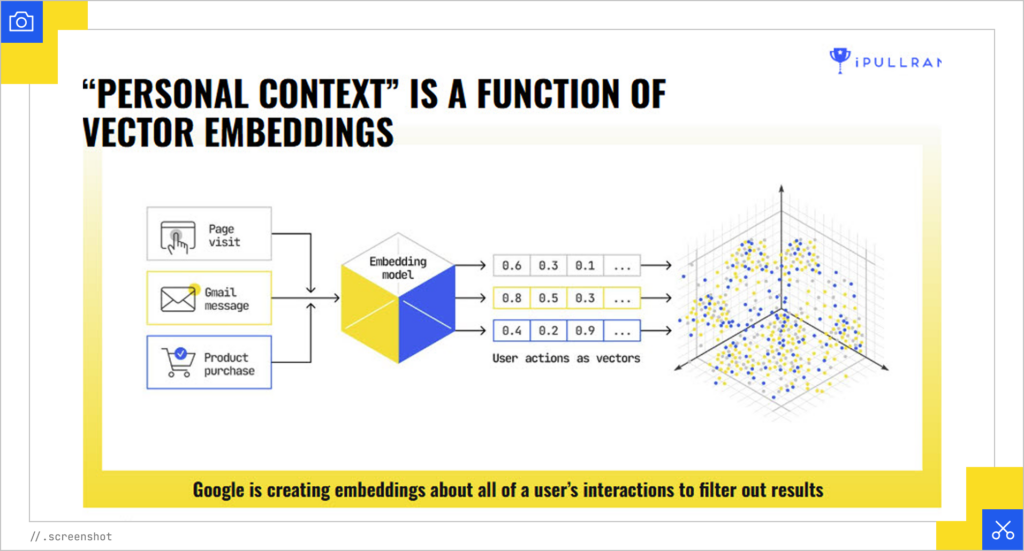
This turns content strategy into optimizing multiple passages across multiple pages, each tailored to different potential queries, so you have more opportunities to make it through reasoning chains.
In other words, it’s not just about your site. It might be from other earned or rented sites like:
- LinkedIn, Reddit, YouTube, and other social media sites (Instagram posts are rumored to be indexed soon)
- Retailers, Google Merchant Feed, Review sites
- News sites, Industry Trade sites
Right now, there’s no plug-and-play tool that is built for this kind of chunking and passage-level optimization. You’ll need your own tools to handle semantic chunking and relevance calculation, and your own strategy for how those chunks are distributed across the web.
Relevance Engineering Strategies
In order to engineer relevance for visibility in LLMs, we need to focus on matrixed strategies.
- How do you rank for primary queries and synthetic queries?
- And how do you make your content perform better in pipelines than your competitors?
- Can you optimize properties that you have minimal control over?

Before you start optimizing your passages, you need to obtain the AI Mode data. For now, you need to build your own tools, but the industry is trying to keep up. We’re seeing tools that are starting to capture (scrape) the data, which you can then vectorize and reverse engineer.
Two vendors that have been quick to offer these capabilities are DemandSphere and FetchSERP.
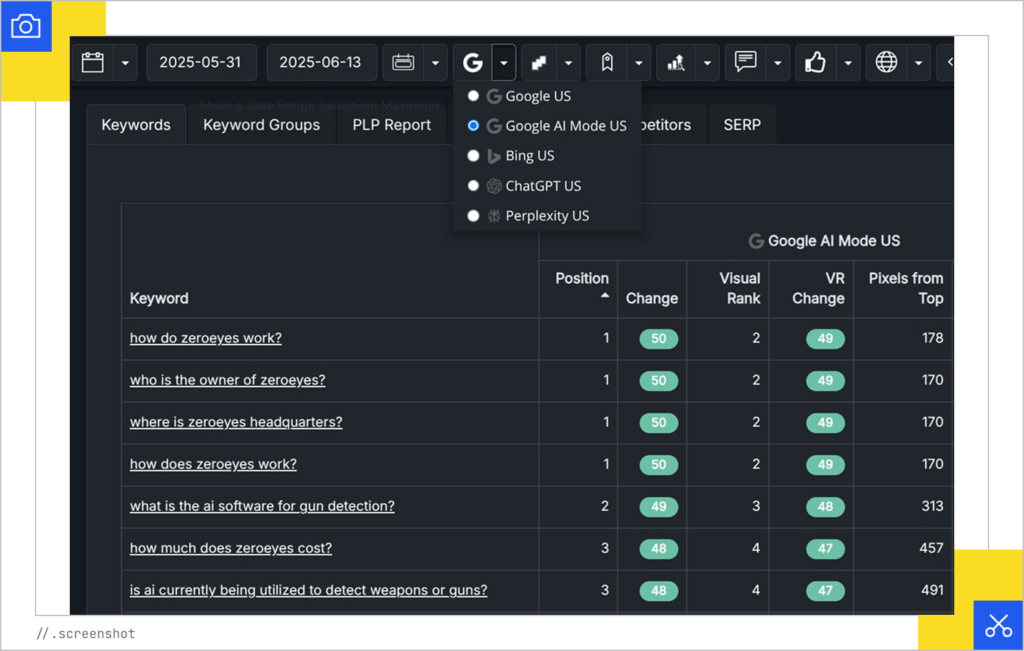
DemandSphere has already added it to their interface.
You need chunking strategies for your content.

Break Your Content into Clear Semantic Units

LLMs retrieve and reason over small chunks of text, not whole documents. Large, undifferentiated text blocks confuse chunking algorithms and lead to retrieval failures. Breaking content into clearly marked sections, paragraphs, and headings ensures more meaningful and retrievable units.
Write in Semantic Triples
Search engines extract features from content through an understanding of semantic triples. The Subject-Predicate-Object relationships can be expressed in the same way as structured data. So, engineer your content in this way.
Don't Write Vague Statements - Be Specific and Unique
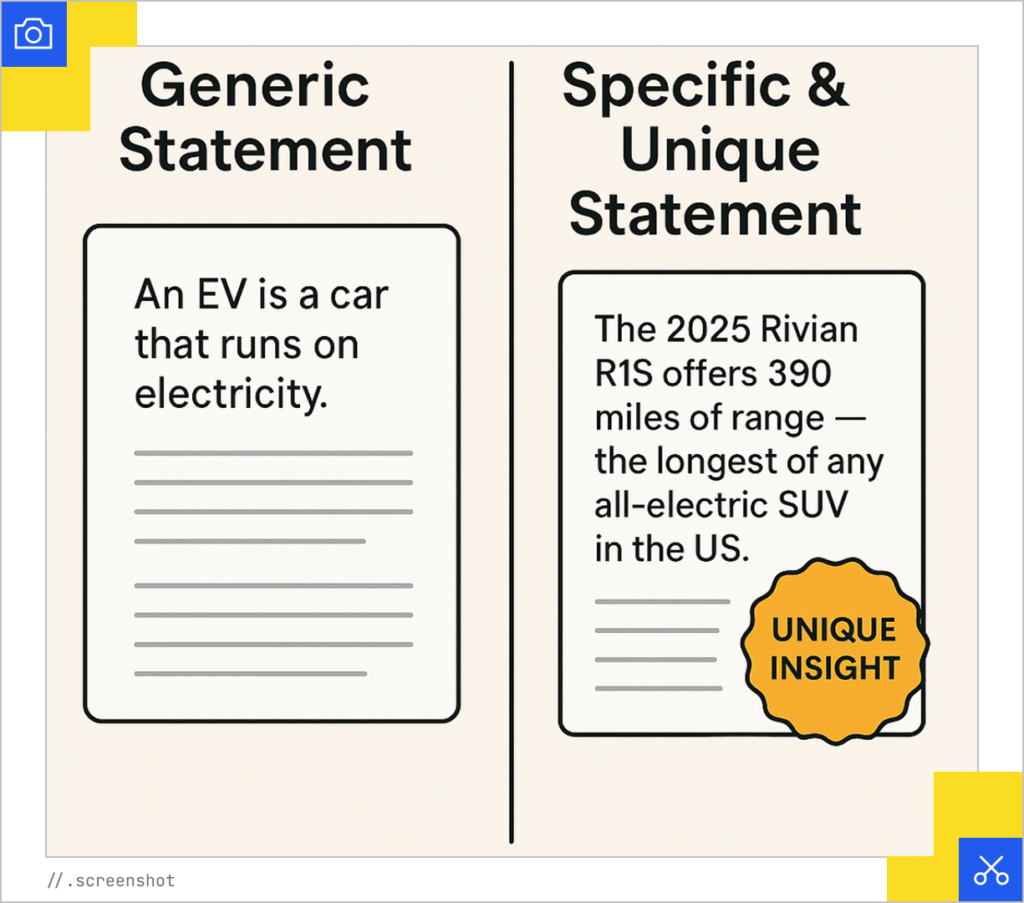
LLMs seek salient, distinctive, non-generic content to surface in answers. Redundant or boilerplate content is more likely to be filtered out.
Use Data in Your Sentences
LLMs often prioritize precise data points and statements of fact in their synthesis. Content that clearly embeds verifiable data is more likely to be selected and cited. Use data to encourage models to extract your data points for their summaries.
Improve Readability
LLMs favor content that is easily parsed and understood. Complex sentence structures, jargon, and poor readability reduce the likelihood of a passage being used. Have a good user experience and readability on your page.
Spread Your Message Beyond Your Site
The retrieval layer behind LLMs favors content corroborated across multiple sources. Key facts and statements should appear not just on your site, but across authoritative, independent domains. Spread your message beyond your website and ensure your message aligns everywhere (LinkedIn, press releases, guest posts, etc.).
Embrace Topical Clustering
LLMs reason over multiple related passages. Structuring content as a topical cluster connected through clear linking and consistent terminology improves retrieval and coherence.
Diversify Your Content Formats

Conversational search surfaces are multimodal. Due to the ubiquity of generative AI for text, there is no moat around text content.
Create content in image, video, and audio formats where there are limited assets, and you will likely experience advantages in the query space. If LLMs determine that the best answer online is written in Japanese, it will translate it and feed it to the language model.
Enter Agentic AI
Andrea Volpini took the conversation a step further and said we’re entering the age of agentic AI in which generative models act like agents, not just tools. In addition to responding to prompts, these systems perform tasks, communicate with each other, and generate insights.

This is the vision behind the agentic web. Instead of optimizing content for human users alone, we’re now also building it for AI agents to consume, interpret, and act on. But this doesn’t mean the immediate end of human-driven SEO. We’ll just need to design systems that feed both people and machines.
The concept isn’t new, though, and Andrea said we’ve been preparing for AI agents for the past 25 years.
What really matters now is your semantic layer to control the AI experience and engineer relevancy. Think of it as building a memory for your brand that AI can access over time. Whether it’s Google’s Gemini or your internal AI tools, that memory helps systems understand your products, your content, and your relevance to user intent.
“We are technically in a post-human internet.”
- Andrea Volpini
Optimizing for a Post-Human Internet
This isn’t sci-fi and it’s not as scary as it sounds. In fact, it’s a huge opportunity to learn the language of AI.
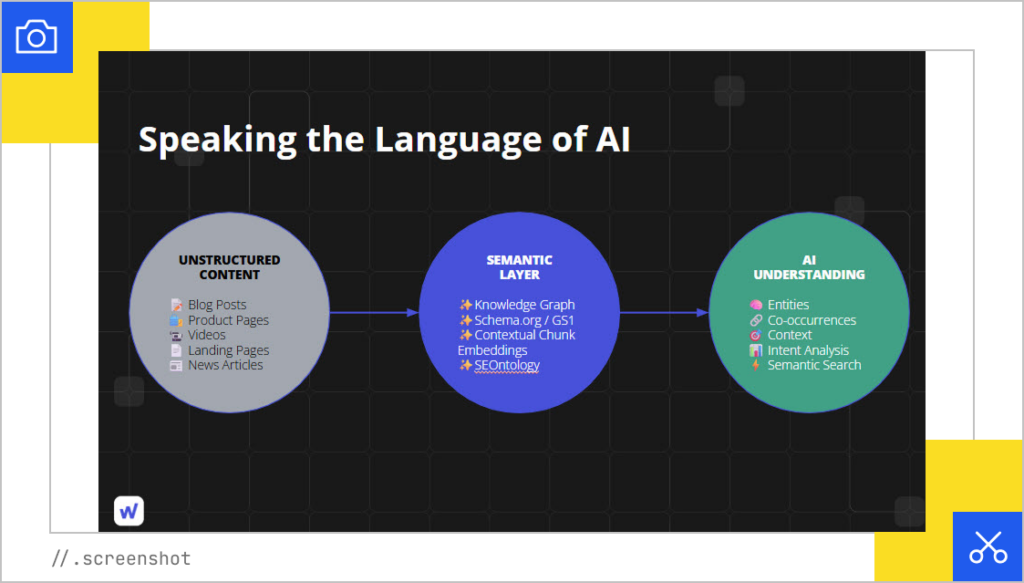
Success today isn’t about a single ranking factor. It’s about being memorable to machines because your next client will be an AI agent. That means:
- Preparing AI-ready data.
- Creating self-reinforcing content loops.
- Being memorable.
- Optimizing for passages, not just pages.
- Focusing on intents and customer personas.
Andrea also offered some advice for content writers that mirrored the guidance from Mike:
- Build very clear and skimmable chunks.
- Write descriptive headings, short paragraphs, bullet points and tables.
- Focus on a single entity semantically aligned with user intent.
Working with AI Agents
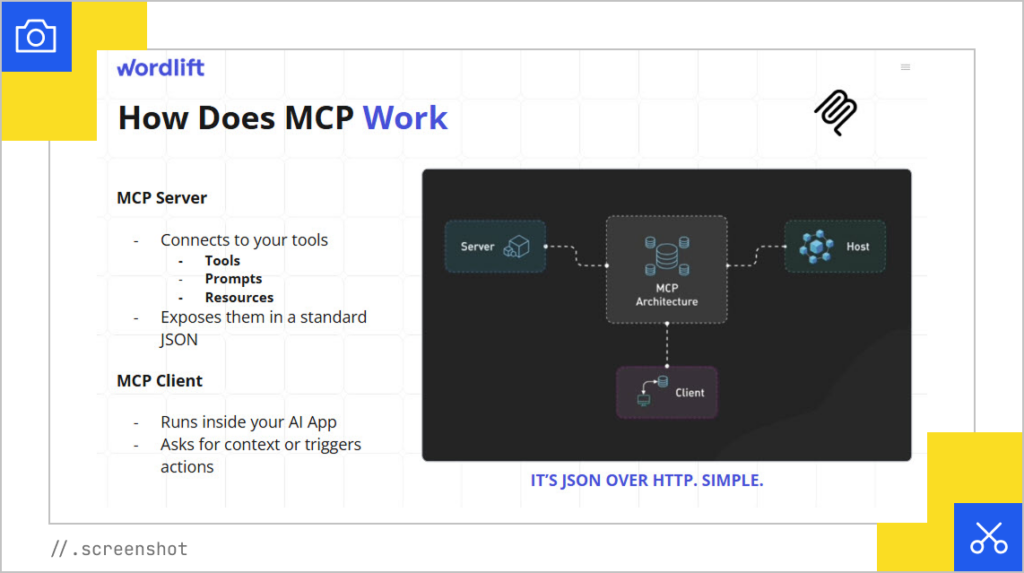
Andrea discussed SEOntology, which is a tool that helps AI agents take on SEO and marketing tasks. He also talked about the model context prodigal (MCP), which can transform static content into a dynamic AI experience. You can run a prompt, then it speaks with the MCP to create multiple agents, and then divides the work between them to complete a task.
If you’re interested in seeing if your click-through-rate drop has been caused by the appearance of AI Overviews, you might have one AI agent check if a SERP has an AI Overview, while another digs into GSC for traffic drops, and others simulate AI Mode behavior to surface potential visibility losses. You could have 5 to 10 agents running in tandem to diagnose and solve problems.
Andrea also recommended some type of query fan-out simulator to help you with content gaps and visibility.
What You Can Do Now
The Q&A portion of the webinar surfaced another great list of Relevance Engineering recommendations that you can do right now to improve your visibility in LLMs and AI Mode:
- Revamp Legacy Content: Go back into older content on your site and prune or edit it. Break up walls of text. Improve headings. Identify synthetic queries using fanout simulation and make sure your content aligns with those queries. Improve clarity. Use semantic triples. You know the drill by now.
- Experiment with Agentic Thinking: Test out multi-agent frameworks. Use tools that simulate how AI Mode breaks down content. Think about how you want to train your AI tools and curate your data accordingly.
- Content Length: It’s not about how long or short your content is. It’s about the density and clarity of your passages, as well as the diversity of your content. A single page might satisfy multiple synthetic queries but sometimes LLMs won’t use the same page over and over.
- Paid Search and AI: Google is also bringing generative AI into PPC for targeting. It’s no longer about keywords but aligning your content with landing pages, and the system will generate creative assets based on that content. Google is investing a lot in Performance Max to optimize results and for personalization.
Preparing for the Future of Search
The traditional SEO mindset isn’t going to cut it anymore. Now that we’re optimizing for passage-level relevance in a probabilistic, agent-driven, hyper-personalized search experience, we need Relevance Engineering practices to take us into the future.
The earlier we start speaking the language of AI, the better positioned we’ll be to stay visible and valuable. While the tools, terminology, and tactics might feel overwhelming right now, relevance is about being the most useful, structured, and memorable signal in a sea of noise.
As Andrea said: “It’s an amazing opportunity and it’s fun, but it doesn’t need to be scary.”







