“Most kings get their heads cut off”
Artist Jean-Michel Basquiat encapsulates the human desire to kill off the person (or entity) in power. Empires rise and fall. No king stays at the top forever.
In the world of search, Google is king and it’s been that way for a long time.
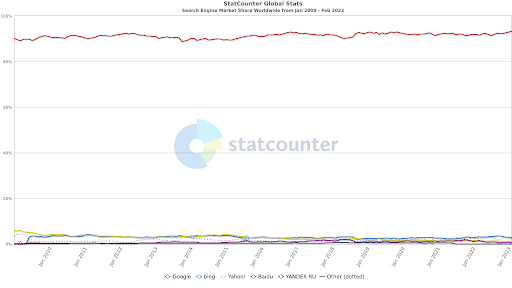
If you’ve read an ‘SEO is dead’ opinion piece at any point in recent years then you know exactly what I’m talking about. Or maybe you’ve heard that social media app TikTok is going to bury Google because newer generations have found it to be a better search experience. All of these conversations follow a specific trend.
The king must die.
In a year where generative AI has become the topic of almost every conversation across multiple industries, it’s no surprise that Open AI’s ChatGPT is the latest (and probably greatest) threat to Google’s search product we’ve seen in a while.
As formidable as some of these opponents may seem in this rapidly growing AI space, to quote one of my favorite television series, The Wire, “You come at the king, you best not miss.”

Frankly, I don’t anticipate Google losing the war, but for those hoping to steal market share from the tech giant, a little disruption could lead to a billion dollar payday.
What We Know So Far About Google’s Generative AI Products
Google isn’t just twiddling their thumbs while the rest of us have a blast toying with chatbots and examining large language models.
In fact, they’ve mentioned a few times that they believe AI to be the most critical means of carrying out their objective of organizing the world’s knowledge and making it universally accessible and valuable.
“AI is the most profound technology we are working on today. Whether it’s helping doctors detect diseases earlier or enabling people to access information in their own language, AI helps people, businesses and communities unlock their potential. And it opens up new opportunities that could significantly improve billions of lives. That’s why we re-oriented the company around AI six years ago — and why we see it as the most important way we can deliver on our mission: to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
In early February 2023, Google announced Bard, a new conversational AI tool that blends the depth of the world’s information with the strength and creativity of massive language models.
The goal from the start has been to make the transition into this new AI-driven world simple, secure, and scalable for users. Sounds incredible, right? So why are so many people pushing for Google to be taken out to pasture? Let’s talk about it.
The Reception of Bard
Google’s rollout of Bard hasn’t exactly gone as planned. People on social media and analysts were quick to point out Bard’s inaccuracies and the lack of details about how it would integrate with Google’s search engine.
Google, $GOOGL, AI chatbot Bard gave inaccurate information in company advertisement, per Reuters.
— unusual_whales (@unusual_whales) February 8, 2023
It is now down -4%.
New: Google published an ad in which its new AI chatbot Bard served up inaccurate information.
— Martin Coulter (@MartinJBCoulter) February 8, 2023
The error was spotted just as the tech giant unveiled its new tool at a launch event in Paris.https://t.co/7ivhC7rzMZ
Google’s much-hyped new AI chatbot tool Bard, which has yet to be released to the public, is already being called out for an inaccurate response it produced in a demo this week https://t.co/dmsHaoBhFp pic.twitter.com/FIXQ2llQNi
— CNN (@CNN) February 8, 2023
Let’s just say it wasn’t a good look. As a result of how social media users and publications responded to the Bard blunder, shares of Google’s parent company Alphabet fell 7.4%, losing the equivalent of $100 billion in market value.
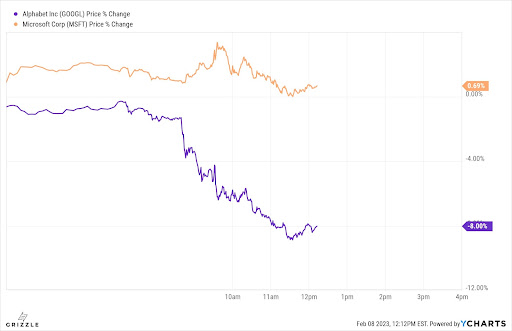
Shortly after the initial announcement of Bard in early February, Google’s VP of Search, Prabhakar Raghavan, sent out an email to Google personnel requesting they rewrite Bard comments on subjects they were most knowledgeable in according to reports. Google says the chatbot “learns best by example,” thus providing it with factual responses could be helpful in fine-tuning the tool.
On March 21st, Google began granting access to users for a standalone chat version of Bard via waitlist. For some who have been following the AI space, this was an opportunity to get a closer look at what Bard can really do. For others, this was a prime opportunity to get a comparison of two AI juggernauts: Bard vs ChatGPT.
My very first use of Bard. What do we think?
— Garrett Sussman ☕️🔎 (@garrettsussman) March 21, 2023
Prompt:
"Create an analogy for search engine optimization based on the career of Allen Iverson" pic.twitter.com/SGeYipWRAA
Google Bard can’t write a function that adds two numbers pic.twitter.com/t1B1WHRPrr
— Jane Manchun Wong (@wongmjane) March 21, 2023
As for their competitors, Microsoft may be investing $10 billion into ChatGPT, but Google’s reputation and resources give them an edge. After all, they’re a company that’s always been willing to take risks and think outside the box. So, while Bard may have been a bit of a misstep, we can’t count Google out just yet.
Project MAGI
Google’s latest AI announcement, Project Magi, is all about making search more personalized and conversational for users. With over 160 Googlers on the team, one initiative is to add new AI-based features to the existing Google Search, such as allowing users to complete transactions and answer questions about software coding. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
The ultimate goal of Project Magi is to create an all-new search engine that uses AI technology to anticipate users’ needs and provide them with the information they’re looking for in a more natural and conversational way. Similar to ChatGPT, an LLM you can speak to, ask questions, and surface information, frameworks, new ideas, and more.
Project Magi is just one of several AI-powered projects that Google is working on. Google Earth’s mapping technology is also getting an AI upgrade, which could make it even easier to explore the world from your computer screen. And if you’re searching for images on Google, you may start seeing more AI-generated results in the future.
The commitment goes beyond search and images. Google also hopes to use AI to teach users new languages through open-ended text conversations. Imagine having a virtual conversation partner who can help you practice your language skills anytime, anywhere.
With Project Magi and these other AI-powered projects, it’s clear that Google looking to be proactive while still remaining unhasty in their approach to AI. And as AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect more intriguing announcements from Google in the future.
BING, ChatGPT, and the Impact on Google
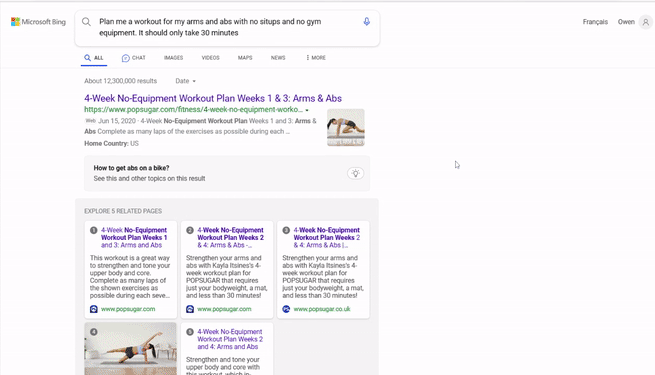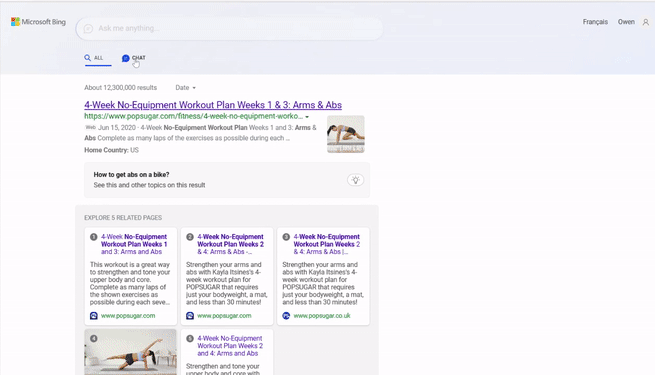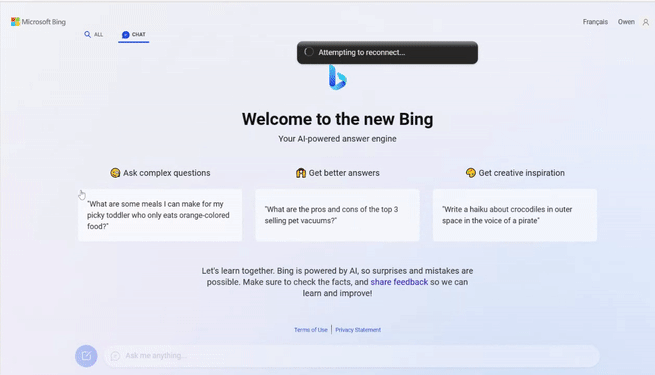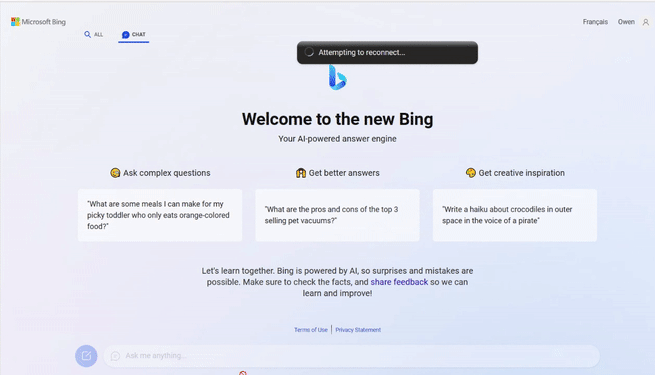
Since Microsoft made the announcement on February 7th of OpenAI’s ChatGPT being integrated with Microsoft’s Bing search engine, it has been a scathing hot topic due to its ability to deliver quick (and sometimes accurate) answers to users’ queries.
This integration has, in a way, reignited the competition between Bing and Google, with some opinions around the internet even claiming that Bing’s answer engine outclasses Google’s search engine. Microsoft and Open AI received high praise for their quick rollout, connection to the internet for real time answers, and the ability to include citations for the generative AI outputs. For many keeping an eye on the generative AI space, this team-up marks a new innovation in the world of search by merging the power & capabilities of ChatGPT with its already existing search engine.
With that said, it hasn’t all been calm seas for Microsoft as the public has been getting acclimated to the tool. They’ve dealt with their fair share of mishaps around inaccurate information and some flat out bizarre outputs since launch and folks have not held back on criticism.
It’s important to keep in mind that while AI-powered answers may be fast, they may not always be accurate or trustworthy.
As Mike King mentioned last year, generative language models such as GPT-1, GPT-2, GPT-3, and T-5 can generate copy based on probabilities of the next word, punctuation, or code in a given sequence. These models do not actually “write” but rather emulate copy based on the number of parameters generated in their training. ChatGPT was trained on billions of documents from 2021 and earlier. LLMs like this are typically trained once and used for long periods of time, meaning that their understanding of language and beliefs is “value-locked” and does not change over time. Users should exercise caution and verify information from multiple sources before relying solely on AI-generated answers.
Despite these shortcomings, there is rapid improvement in the generative AI space. OpenAI recently launched GPT-4, the newest version of the LLM that powers its AI chatbot ChatGPT, on March 14th. GPT-4 offers safer and more useful responses, can accept images as input, has extended text interpretation and outputs, increased factual accuracy, and more advanced reasoning capabilities. As of right now, GPT-4 is only available for ChatGPT Plus users for $20 per month, but OpenAI plans to make the GPT-4 API available to developers via a waitlist.
But what does this mean for Google? As the leader in search engines, they obviously can’t afford to fall behind in the race for AI-powered search capabilities. However, this is business at the end of the day and ROI will always be a consideration. Google will absolutely continue to invest in the development of generative AI, but to what extent will AI generation disrupt Search? What does a modern search engine with generative AI capabilities look like?
Other Opponents In The Ring
NEEVA AI
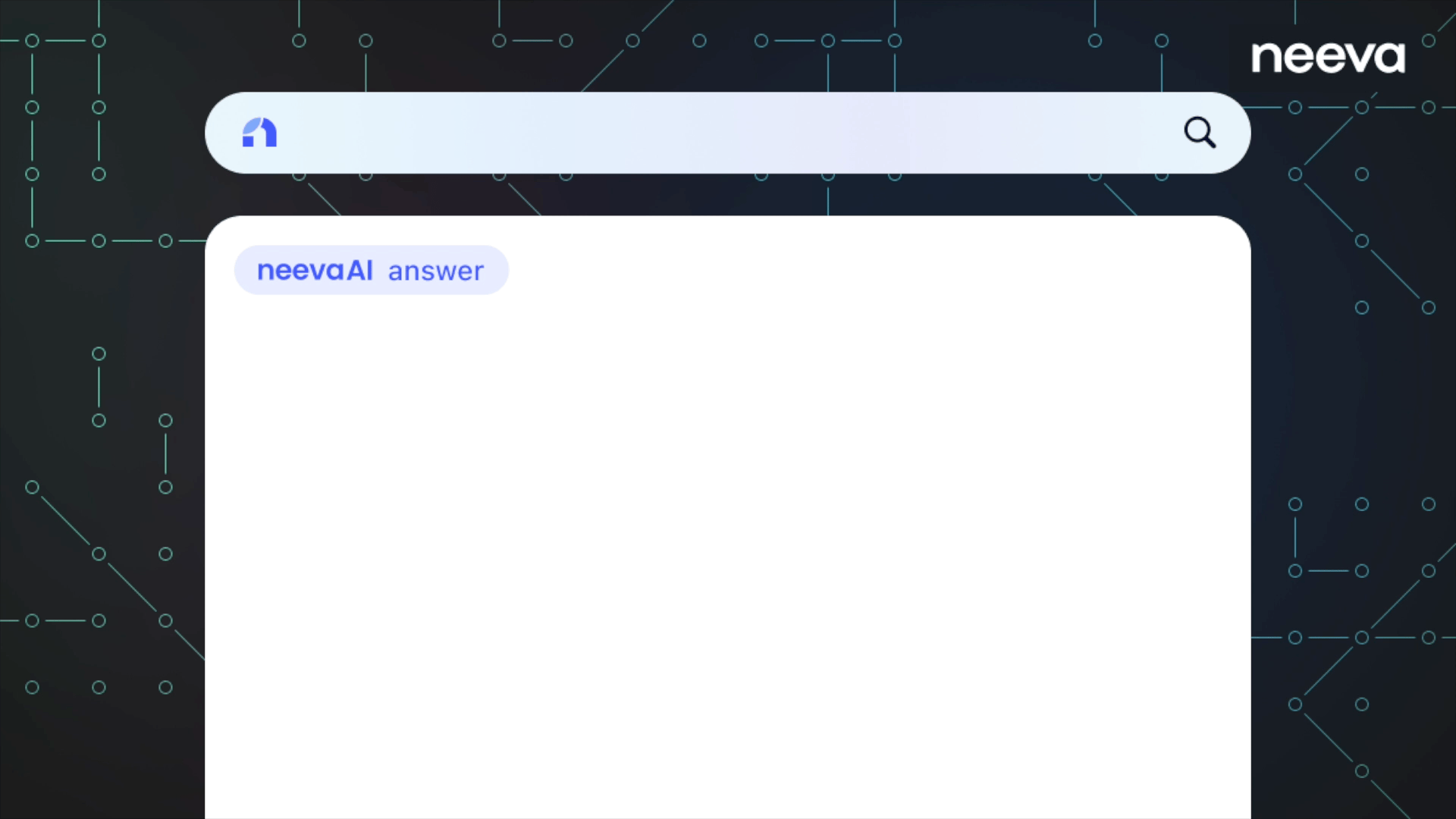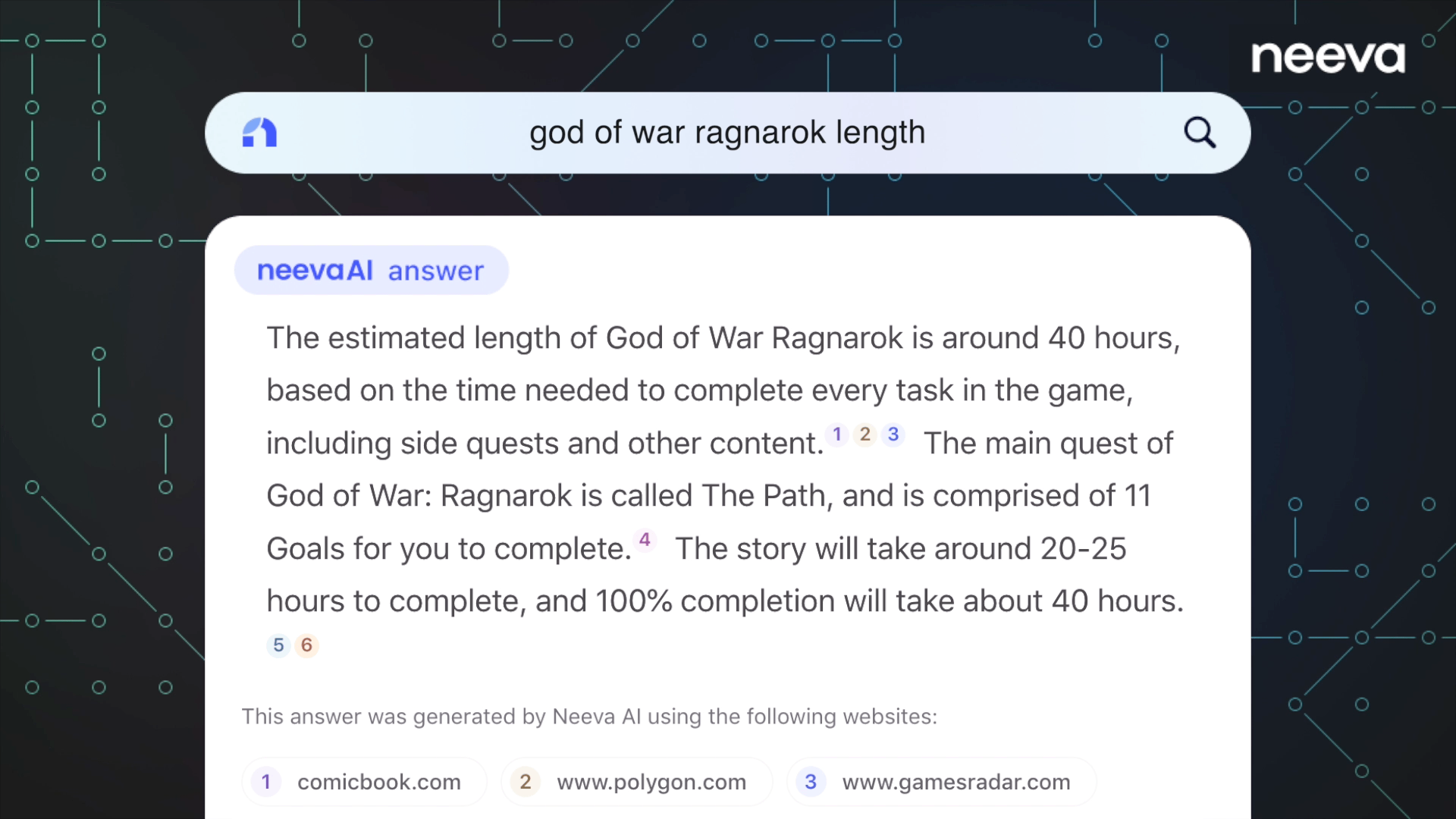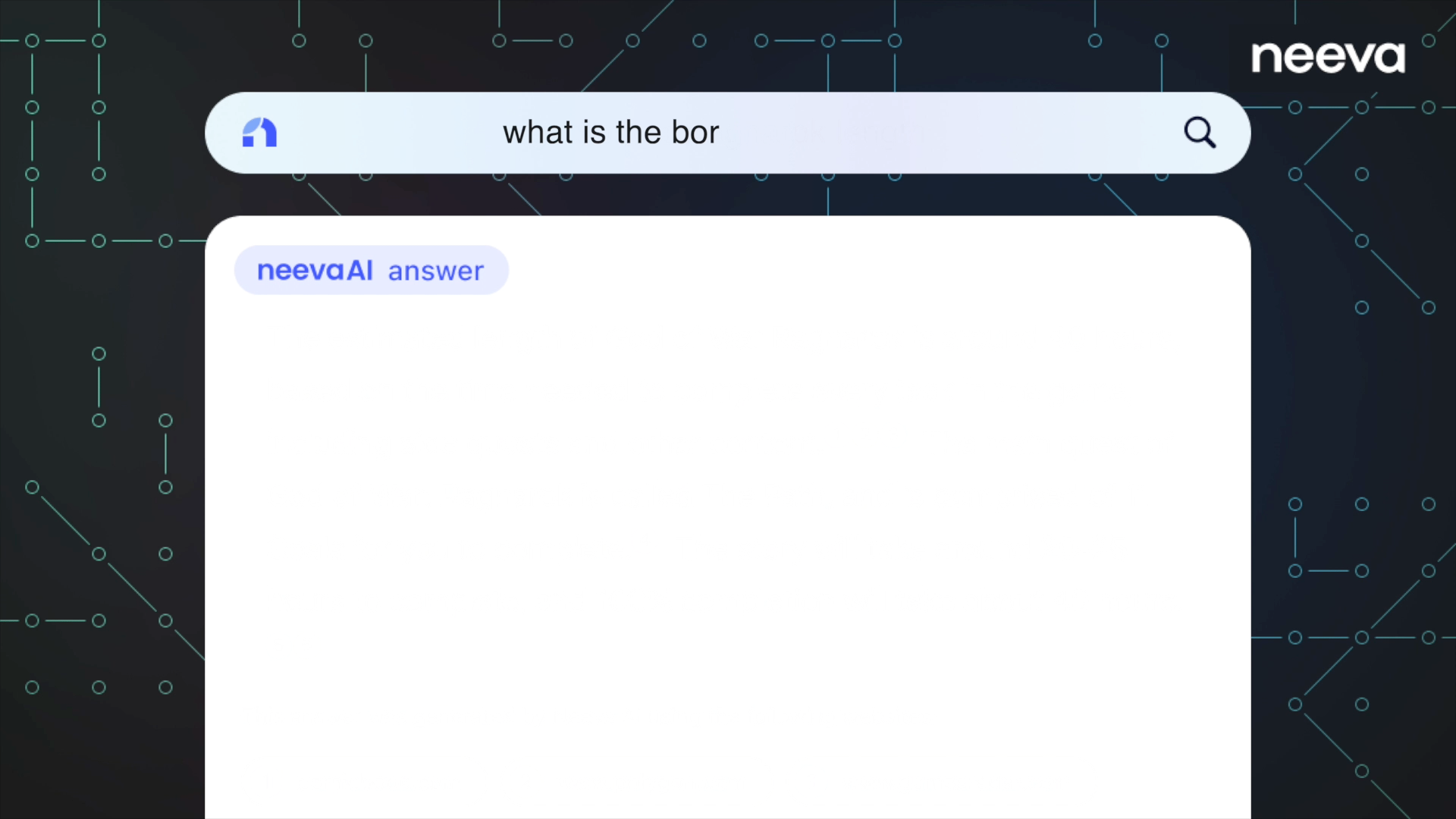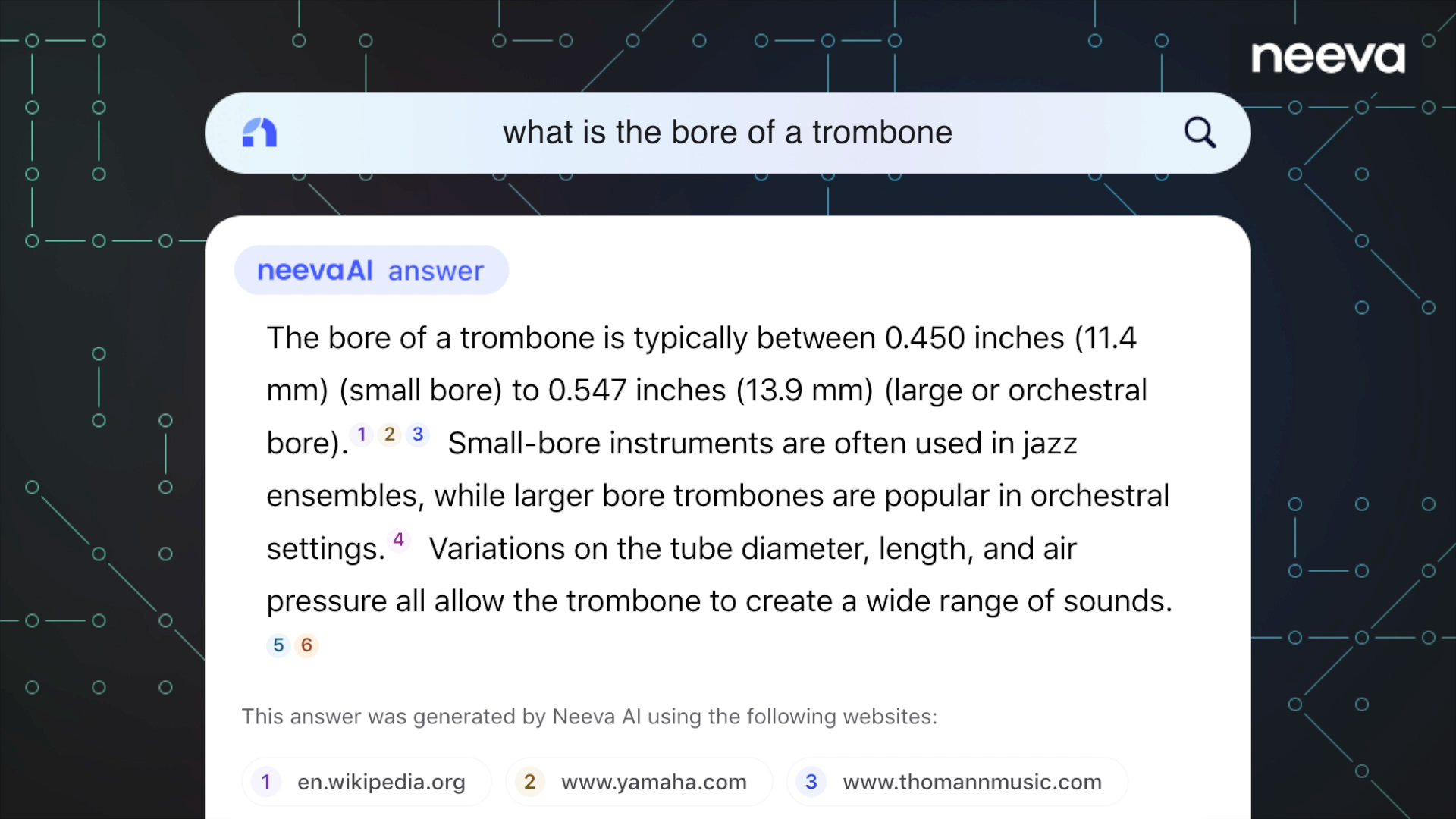
There are others brave enough to challenge Google in the AI search space. One of the more impressive tools is NeevaAI. Neeva, a state-of-the-art search engine originally launched in 2021, recently launched its AI-infused search tool, NeevaAI, internationally to Canada, the UK, Germany, France, and Spain. Neeva’s core selling point is its ad-free environment, with no third-party trackers using personal data to display personalized ads.
Another thing that sets Neeva apart is how it integrates search and AI deep in its core. With AI processing information on the most relevant pages and turning that information into clear and digestible summaries in real time, NeevaAI triggers on the majority of searches. This is a significant advantage over traditional search engines which can be slow and unreliable.
NeevaAI generates responses from multiple cited sources in real-time, promoting transparency and giving those who have published content credit, but for questions that it isn’t equipped to deal with, it defaults to the familiar website-specific links and excerpts for users to peruse and figure out the answer for themselves.
While NeevaAI may not have a big brand name yet, Google should take note of this innovative approach to search. With its resources and reputation, Google still probably has the edge over NeevaAI. However, NeevaAI is a great example of how AI is changing the way we search, and it’s exciting to see what the future holds for this technology.
CLAUDE by Anthropic
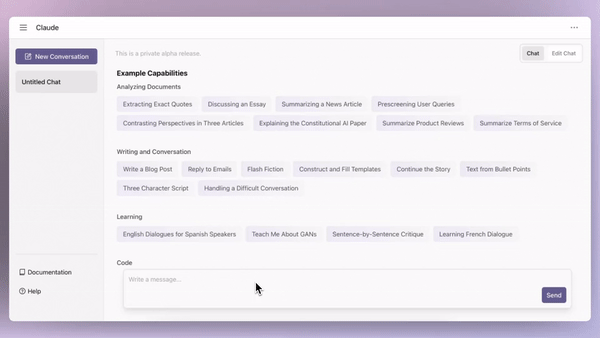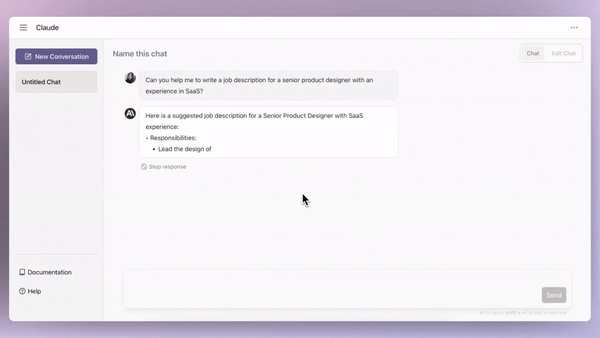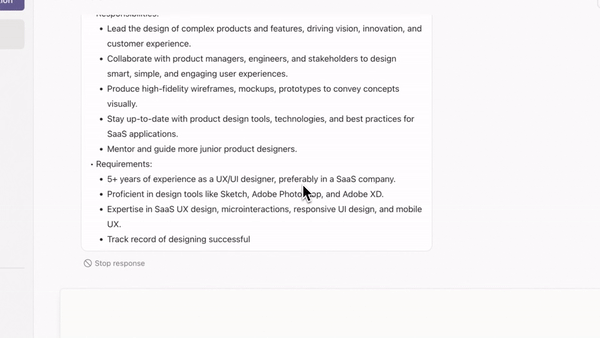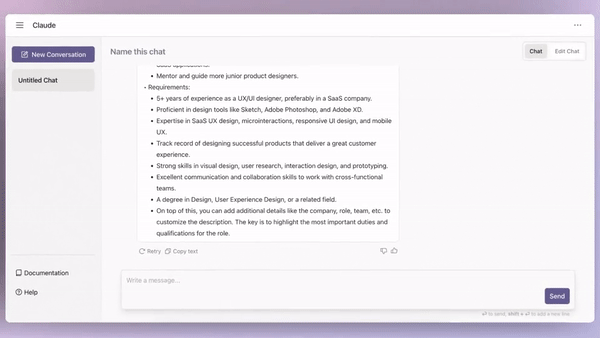
Backed by Google, Anthropic, a company focused on developing safe and reliable AI systems, recently announced the launch of Claude, a next-generation AI assistant capable of a wide range of conversational and text processing tasks. According to Anthropic, Claude was developed with a focus on being helpful, honest, and harmless, which sets it apart from many other AI systems.
Claude has already been tested with key partners like Notion, Quora, and DuckDuckGo in closed alpha, and is now available to the public through a chat interface and API in the developer console. What’s interesting about Claude is that it comes in two versions: Claude and Claude Instant. The latter is a lighter, less expensive, and faster option, which could make it an attractive option for developers looking to integrate AI capabilities into their products.
With Claude, Anthropic is offering a highly customizable AI assistant that can be directed on personality, tone, and behavior. The use cases for Claude are wide-ranging, including summarization, search, creative and collaborative writing, Q&A, and coding. It remains to be seen how widely Claude will be adopted, but it’s clear that Anthropic is positioning itself as a major player in the AI space. Google’s decision to partner with Anthropic and incorporate Claude into its suite of AI tools is a smart move, as it further solidifies its position as a leader in the industry.
The Cost of the AI War
Google has been heavily investing in artificial intelligence (AI), which they see as a critical method to deliver on their aim of organizing the world’s knowledge and making it widely accessible and valuable. Yet, constructing AI models capable of generating human-like dialogues and meaningfully responding to user queries is not inexpensive. The computing requirements of generative AI are pricey, perhaps making it a less profitable endeavor for Google in the long term.
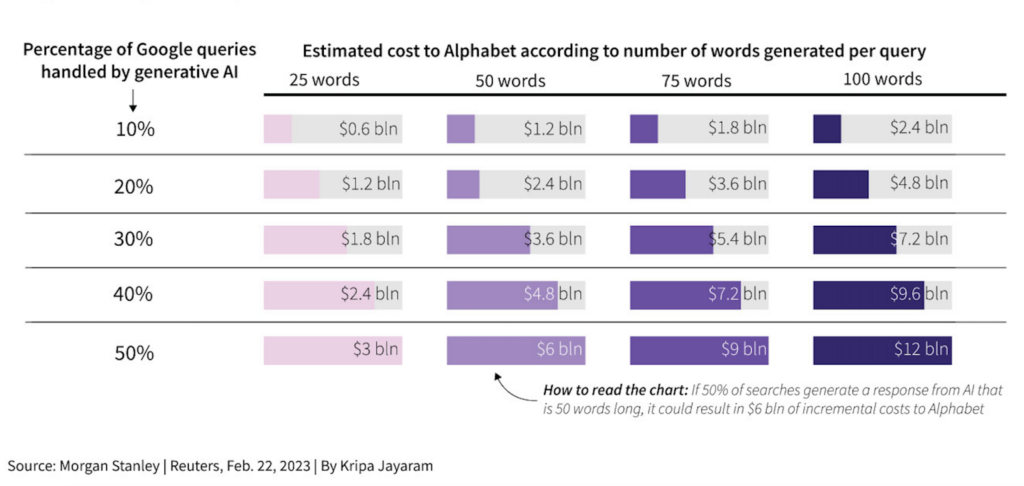
Despite the high cost of generative AI, Google still remains optimistic in its efforts to bring the latest AI advancements into its products, starting with Search. By integrating AI technology into Search and other parts of the Google ecosystem, Google hopes to deepen people’s understanding of information and turn it into useful knowledge more efficiently.
The cost of a ChatGPT query is estimated to be around 2 cents, which is a steep premium compared to traditional web searches. As Microsoft attempts to reimagine aspects of search with the integration of Bing and ChatGPT, they are effectively luring Google into little skirmishes that will be difficult for Google to win.
More Google. More AI.
If there’s one thing Google is known for, it’s pushing the boundaries of technology. Their latest announcement to bring the power of generative AI to developers and businesses through Google Cloud and MakerSuite is just another example of this.
With the PaLM API and MakerSuite, Google is making generative AI more approachable for developers to prototype and explore new applications. And with new generative AI capabilities in Google Cloud, businesses can access enterprise-level safety, security, and privacy while integrating with existing Cloud solutions.
This isn’t just for developers and businesses. Google is also bringing generative AI features to Google Workspace, with instant draft generation in Gmail and Google Docs. Think about the possibility of being able to write emails and documents in the tools you already use daily with ease and efficiency, thanks to the power of AI.
Of course, with great power comes great responsibility, and Google is taking that seriously. They’re inviting external and internal testers to pressure test new experiences, and following AI principles to guide their work.
With all these advancements, it’s clear that Google is betting big on AI. And if anyone can bounce back from what some might describe as a fumble with the rollout of Bard, it’s likely to be Google.
At the end of the day, it’s still Google.
Google has been using AI technology for a while now, and they’ve integrated it into many of their products that we use every day, like search.
- Google Maps – Google applies artificial intelligence and machine learning to create high-quality maps quickly for its Street View images
- Gmail – Gmail suggests replies to the email you’re reading with the Smart Reply feature. Thanks to AI technology like natural language processing, the system can “understand” what is typed (NLP).
- Pixel – Google Tensor, the custom-built chip inside of Google’s Pixel mobile phone allows for new experiences that require state-of-the-art machine learning, such as
- Assistant voice typing
- Live Translate
- 1 Motion Mode
- Face Unblur.
- Google Cloud – You can utilize Google’s Vertex AI (a machine learning (ML) platform) in Google Cloud Console to train and deploy ML models and AI applications.
- YouTube – Youtube uses a two-facing AI algorithm to provide recommendations to users based on its understanding of the user’s history and comparing a user’s history with other users on the platform.
But what really sets Google apart is its ability to keep up with the times and continuously push the boundaries. It’s no wonder that Google Search still dominates the market, generating more than 50% of Alphabet’s yearly revenue.
With the buzz around ChatGPT and Microsoft’s investment in AI, as well as other competitors like Neeva, Alphabet has even more motivation to bring new and innovative AI solutions to the market.
Think of Google and search the way you think of Lebron James and basketball. In 2016, after a 32-year-old Lebron James delivered the city of Cleveland its first championship in 54 years, a narrative began to grow, “He’s getting old, he can’t keep doing this forever.” This is obviously true, but the conversation may have been premature. At the age of 38, he now sits atop the all-time leading scorers list while averaging 30 ppg. Google is Lebron James.
There are a ton of competitors in the AI space, all of which deserve our attention and respect for their contributions to innovation and implementation in AI technology. With that said, it’s best we remember who Google is, how it got here, and why it will take more than this moment in history to put them down for good.







