The SEO industry lost its collective marbles when AI Overviews made a dramatic appearance to fairly mixed reviews back in May 2024. And Google’s newest experiment, AI Mode, has made an even bigger splash since its release in early March 2025.
AI Overviews utilize retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), knowledge graphs, shopping graphs, and more up-to-date information to provide customized responses for a more conversational and semantic search than the standard Googling of the past (while AI Mode uses the Deep Research paradigm, which is more like a multi-stage RAG).
Suddenly, search results are becoming more personalized and condensed. Zero-click results remove the need to click over to a website to get your information, leading many publishers and content creators to panic about the future of their organic traffic. However, too many search results still suffer from misinformation and hallucinations, like this error that went viral:
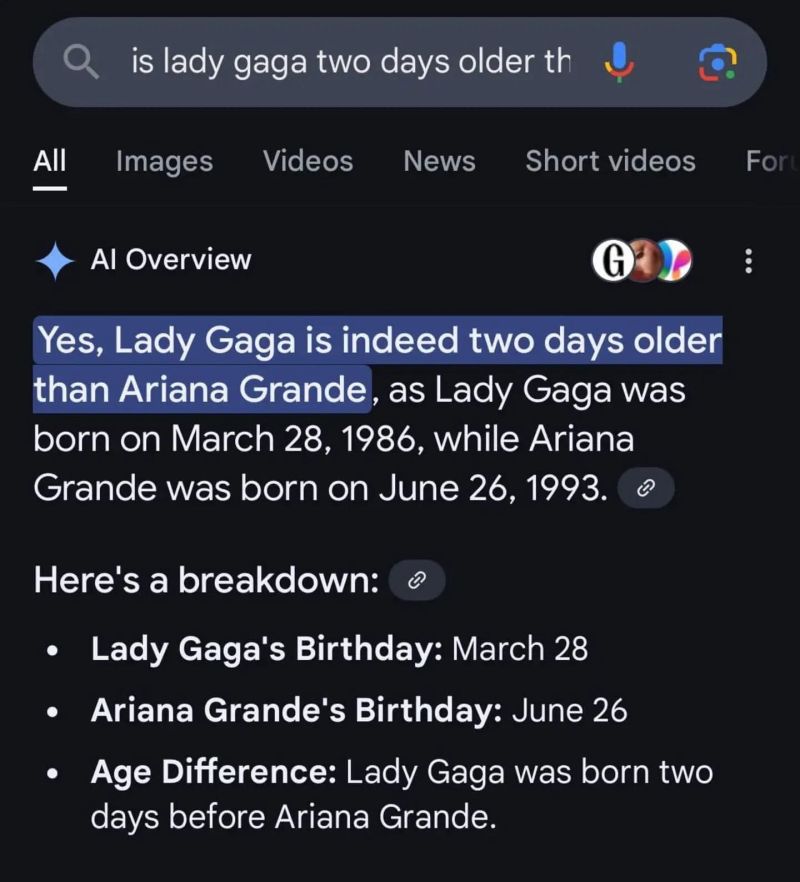
What does this all mean for the future of search? Before looking ahead, we need to understand what RAG is, why it came about, how it works, and how it is transforming SEO strategy right now.
The Cost of Search
A 2023 Google research paper by Andrei Z. Broder and Preston McAfee introduced the concept of the Delphic cost of search:
“Consumers incur many intermingled costs to search: access costs (for a suitable device and internet bandwidth), cognitive costs (to formulate and reformulate the query, parse the search result page, choose relevant results, etc.), interactivity costs (to type, scroll, view, click, listen, and so on), and obviously for all of these activities plus waiting for results and processing them, time costs to task completion.”
In addition, the results of a search are only as good as the query, and the results are often dependent on the context of the searcher. What’s their location? Experience level? End goal? Do they even trust the information they are receiving?
Results could have safety flaws, quality flaws, misinformation, and other negative factors impacting the benefits of search.
In general, people use search engines because they want to quickly and accurately complete tasks and get answers. To accomplish this, search engines must move away from simply focusing on ranking and instead look at the quality of the users’ overall search experience and the relevance of the content it provides.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
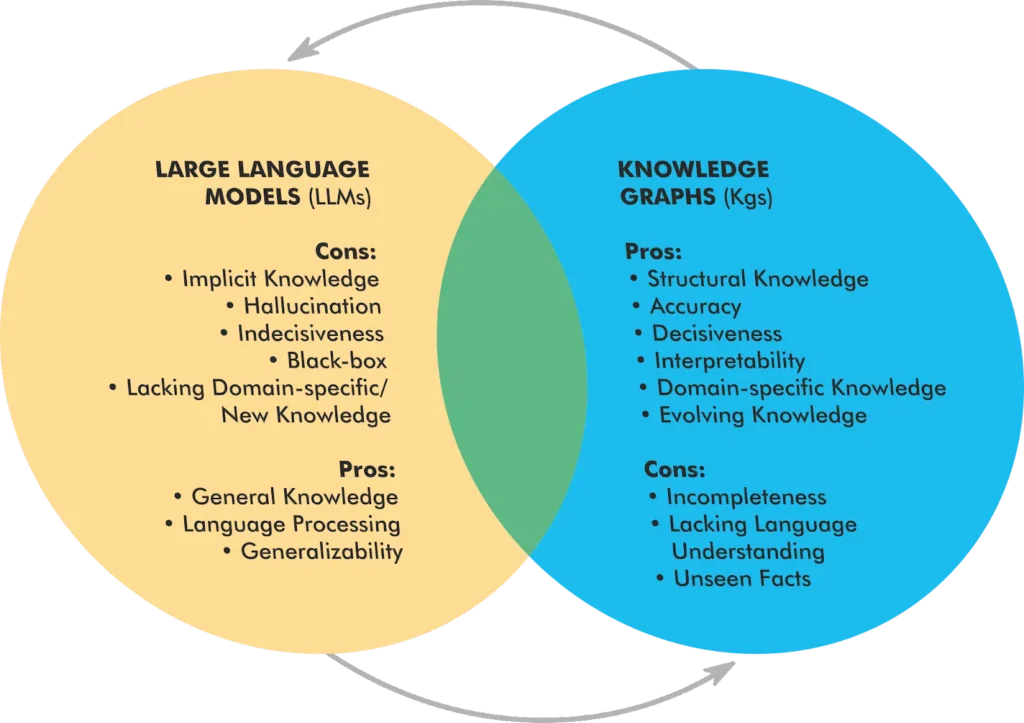
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by retrieving relevant documents or data points to ensure more accurate and context-rich responses. Unlike traditional LLMs that generate text based solely on probability, RAG introduces a more semantic retrieval component aimed at improving the factual correctness and relevance of AI-generated outputs. This is also referred to as grounding.
Grounding allows AI-driven search features like AI Overviews to provide more contextualized answers directly within search results, reducing the need for users to click through to external websites. While the technology isn’t quite there yet (right now, over 60% of AI search results are wrong), it continues to improve, meaning SEOs need to adapt to remain competitive.
When ChatGPT first launched, it relied on a static dataset with a 2021 cut-off. Today, AI Overviews and similar features are no longer limited to their training data and can retrieve real-time, relevant, up-to-date information with the help of RAG before generating responses.
How RAG Works
Mike King has compared RAG to a research assistant capable of retrieving the most relevant information from a vast knowledge base before generating a response. RAG helps that response become more precise, and it can cite sources. A RAG implementation consists of three components:
- Input Encoder: The input prompt is converted into vector embeddings.
- Neural Retriever: Relevant passages are retrieved from indexed documents and knowledge graphs.
- Output Generator: An LLM (such as Gemini, ChatGPT, or Claude) processes this information and generates a refined response.
How relevant are the passages it retrieves? At the time of writing this, it appears that RAG only looks at quantitatively relevant passages (i.e., the cosine similarity of the passage). We don’t know the extent to which AI Overviews takes into consideration other signals like authority and user behavior when it comes to the content it cites and uses in its generation.
What we do know is that it looks at fragments of pages rather than the page as a whole to find the information needed to answer the query. When the search results appear in AI Overviews and you click the source link to see where it came from, it will immediately scroll down the page and take you to the relevant answer, highlighted for visibility. These fragments are also referred to as fraggles, a term coined by Cindy Krum.
This is important to keep in mind when creating content going forward. Instead of focusing on an entire page for each keyword, focus your attention on writing stand-out passages and phrases in your content that answer specific questions that AI Overviews could choose as a fraggle.
Using Graphs
Another improvement on the RAG paradigm is its use of knowledge graphs, which show the connections between entities and organize them. Knowledge graphs help add context to a search to generate a wider range of relevant results. They encompass information on people, data, places, objects, events, and concepts and how they relate to each other.
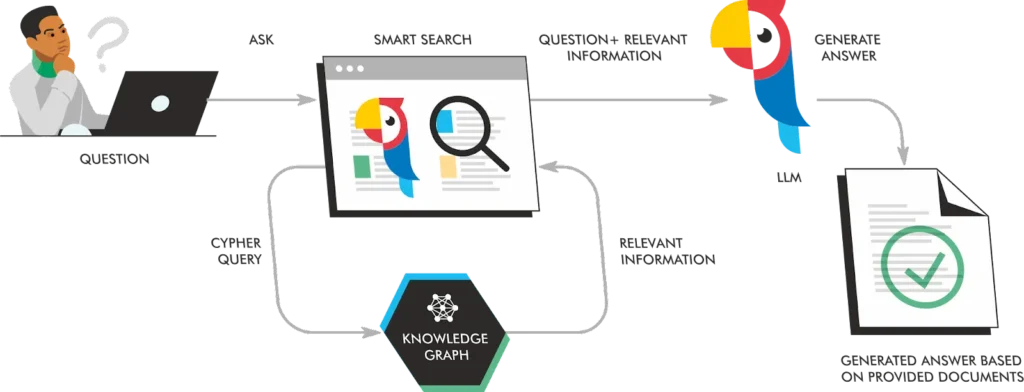
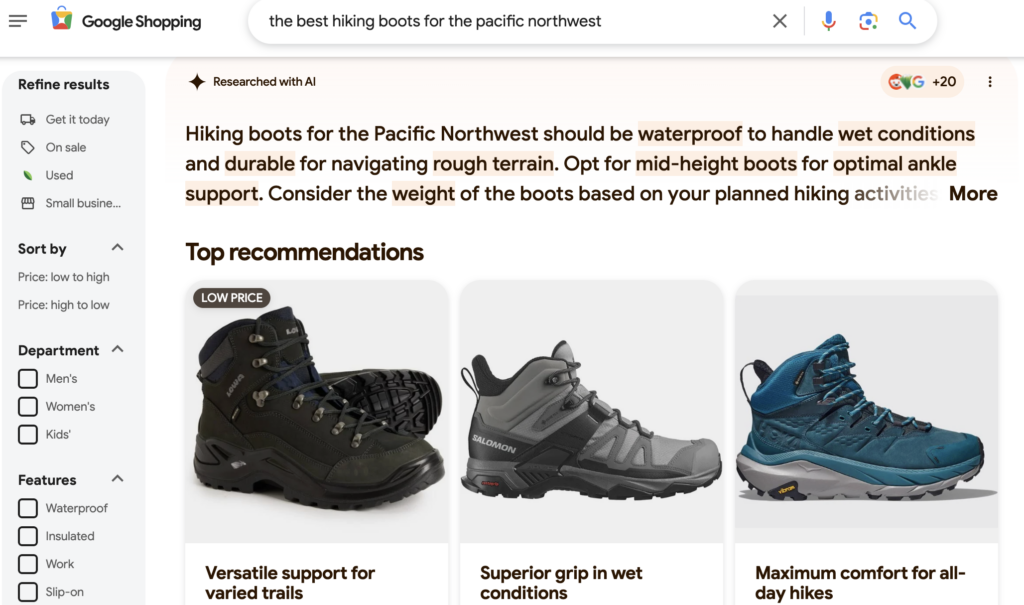
Ecommerce uses its own system of shopping graphs to recommend relevant products to consumers searching for particular items, such as running sneakers or a certain type of kitchen appliance. There are over 35 billion product listings in Google’s shopping graph used to help find products with specific criteria.
It scans these listings and takes relevant images, descriptions, reviews, videos and other data from the web and uses machine learning to understand the relevant, nuanced characteristics. This is why searching for the best hiking boots for the Pacific Northwest leaves you with specific results that are waterproof and good for wet terrain, as shown below:
There have been studies performed that have found that RAG “significantly improves the accuracy and relevance of LLM outputs.” Businesses can also use RAG-enhanced LLMs to get more precise, relevant, and evidence-based insights customized to specific needs.
The Impact of RAG on Search
The main benefit of RAG is better output by extending the knowledge available to the language model. However, accuracy remains a challenge, with disclaimers noting that AI-generated results can still contain errors.
People continue to use AI search models, but understandably still expect to receive the correct information they’re requesting. You don’t want to query the best local vegan restaurants and receive results for steakhouses.
Here are some factors that impact the power of RAG:
- Data: The data input must be up-to-date and accurate to be useful.
- Redundancy: If there’s too much copycat content (as there often is), repetitive and poorly researched content may taint search results.
- Prompt Limits: AI prompts can only be so long, which can limit how well you’re able to describe the information you need.
- Hallucinations: No matter how well you prompt and how accurate the data is, the LLM can still get things wrong.
And here are some aspects of RAG that are changing search behavior significantly by driving less, but more qualified, traffic from the SERP:
- Comprehensive Responses: AI Overviews doesn’t just take content from the top-ranking search results but rather pulls content from related queries. It offers a different, more comprehensive response to the search than traditional search results.
- Location of Results: AI Overviews is a more robust form of the featured snippet with generative text and links to citations. It often takes up the entirety of the above-the-fold content areas, pushing standard search results farther down the page.
- Follow-up Questions: This conversational form of search where you can follow up your prompt with additional related questions has been used in ChatGPT and can now be found in AI Overviews and AI Mode. The Search Generative Experience originally allowed for follow-ups, but they disappeared when Google rolled out AI Overviews publicly. Now AI mode is essentially adding them back.
This is all a departure from standard search results. As users become accustomed to receiving immediate answers to their questions instead of a list of 10 blue links, there is likely to be a significant shift in search behavior and possible negative impacts on organic traffic to websites. Studies have found that AI Overviews appear in the SERPs for 12.7% of queries, and that number will continue to grow.
A recent lawsuit against Google from the company Chegg has opened the door for more organizations to question the impact of AI Overviews on organic traffic to their websites. Chegg accused Google of lost traffic because of AI Overviews, which thereby resulted in a loss of revenue. We will soon see if other companies follow suit.
RAG in Ecommerce and Local Search
RAG is already transforming ecommerce and local search by integrating real-time data into search experiences. This provides more personalized shopping results for consumers.
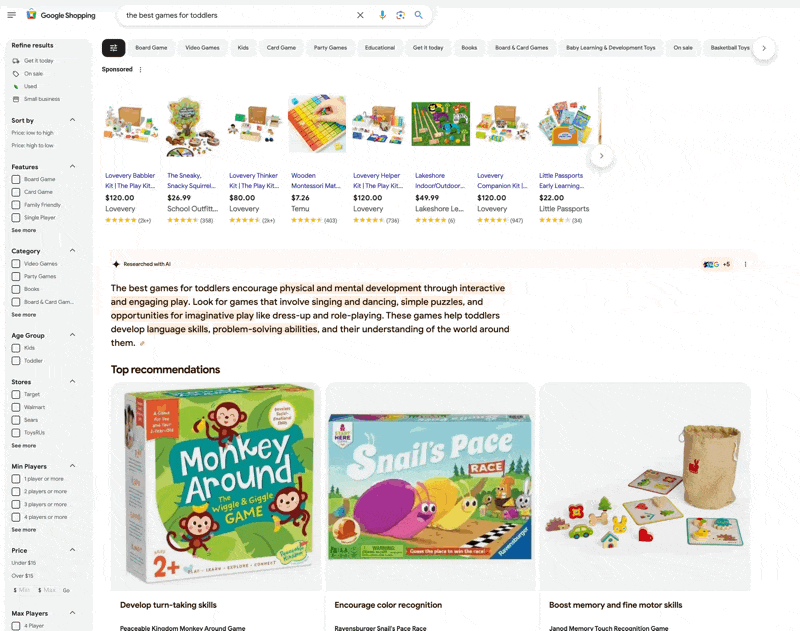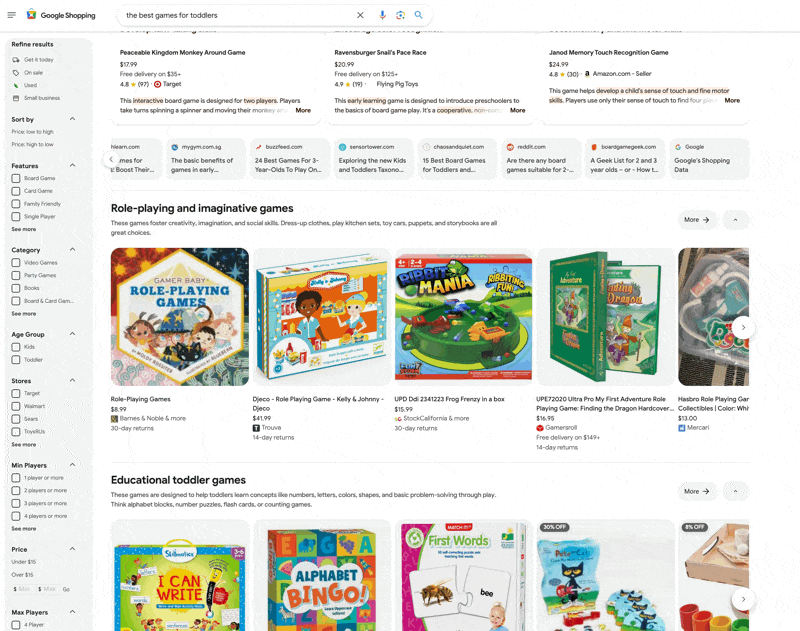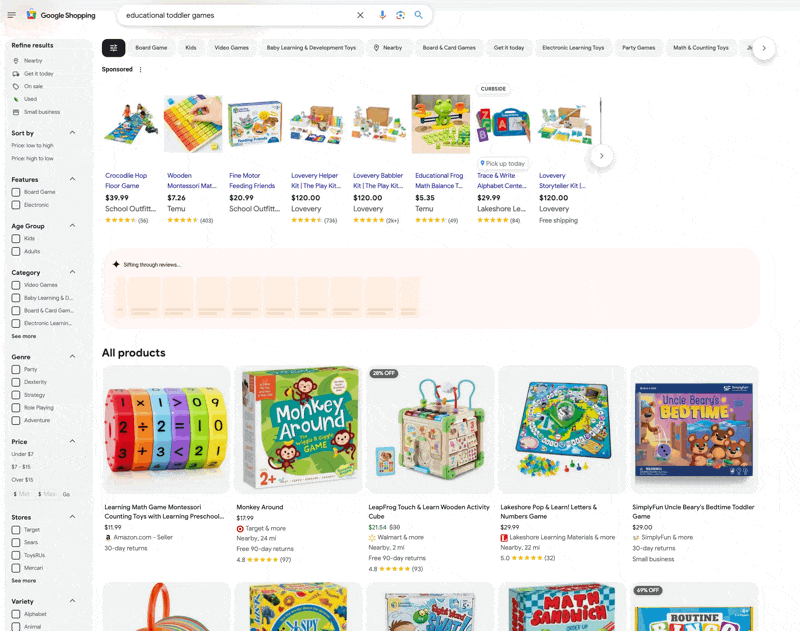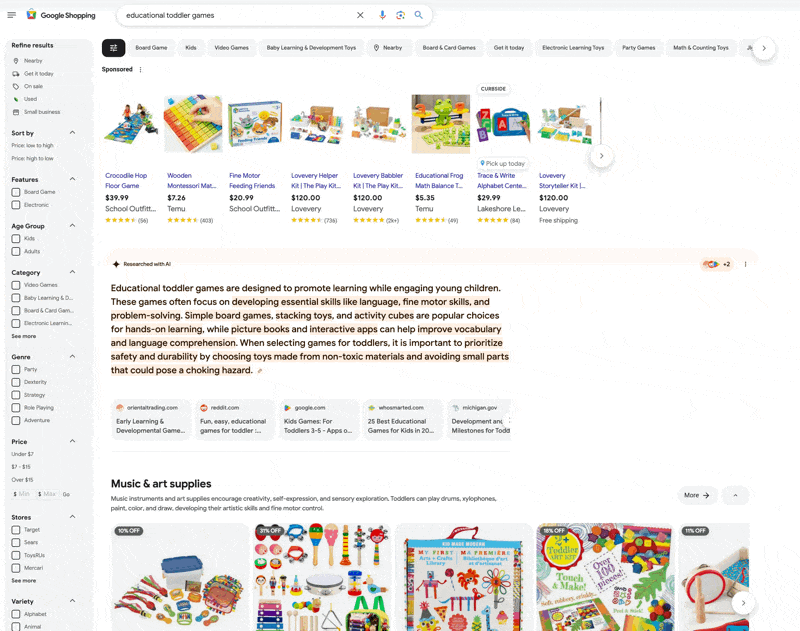
AI Performance Optimization Lead at AMD Eduardo Alvarez writes: “The RAG-based recommendation system redefines personalization by dynamically integrating vast amounts of data, from market trends to individual customer interactions, into the recommendation process. This ensures that product suggestions are relevant and timely, enhancing the shopping experience and fostering stronger customer relationships.”
For SEOs, this means ensuring that businesses and products are properly represented in knowledge graphs and structured data. If AI-driven search engines prioritize structured, real-time information, optimizing for these elements becomes crucial.
How AI Overviews Works (REALM, RETRO and RARR)
The Google Research team first presented an implementation of RAG in their paper, “Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training (REALM),” back in August 2020.
The paper talks about a method of using the masked language model (MLM) approach to do “open-book” question answering using a corpus of documents with a language model.
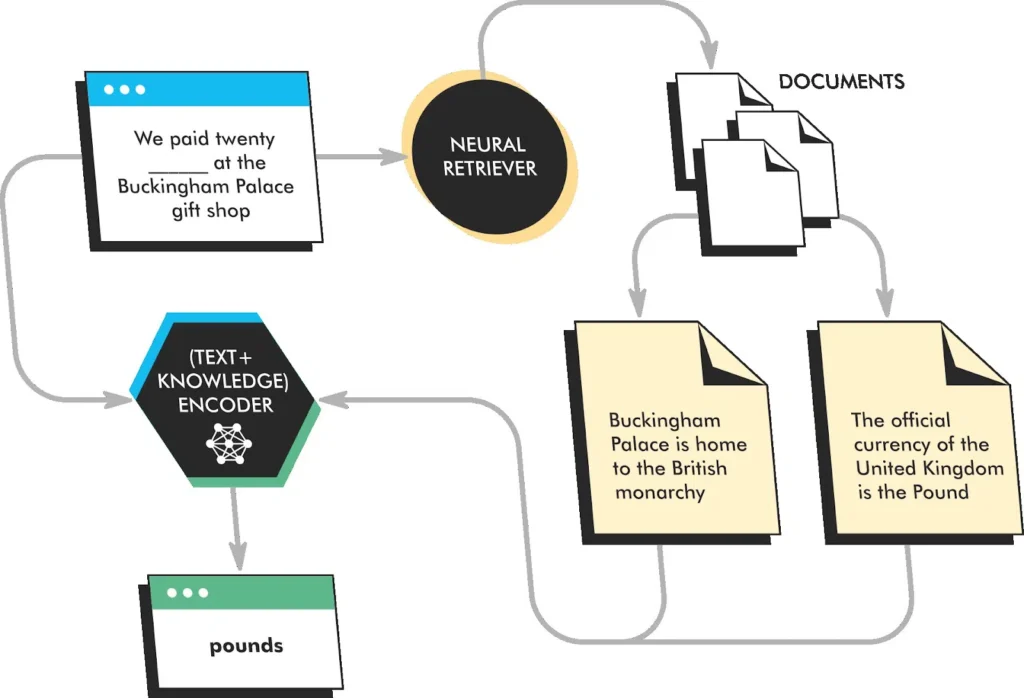
REALM identifies documents and their relevant passages to find the most relevant one for information extraction. It’s trained to predict masked tokens in a sentence, as well as retrieve relevant documents from a corpus and attend to these documents when making predictions. This allows REALM to learn to generate more factually accurate and informative text than traditional language models.
Google’s DeepMind team took this idea further with Retrieval-Enhanced Transformer (RETRO). RETRO is a language model similar to REALM but with a different attention mechanism.
It views the retrieved documents in a more hierarchical way, allowing it to better understand the context of the documents and provide text that is more fluent and coherent.
Following RETRO, the teams developed an approach called Retrofit Attribution using Research and Revision (RARR) to help validate and implement the output of an LLM and cite sources.
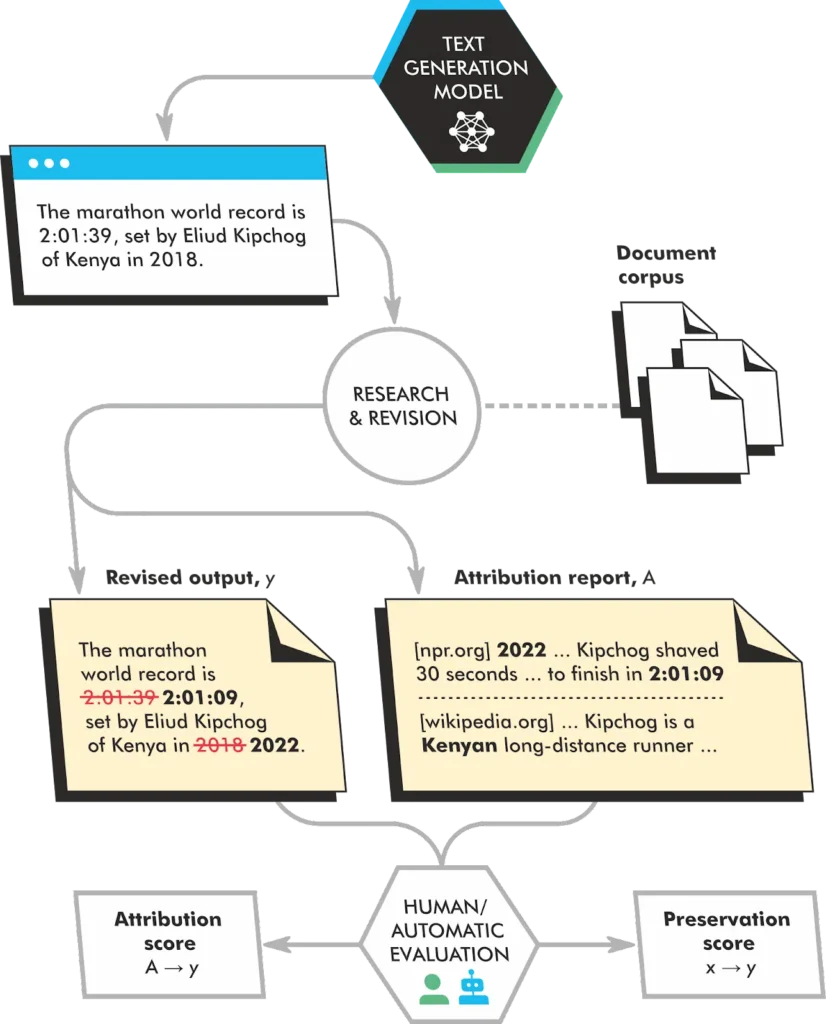
RARR is a different approach to language modeling as it doesn’t generate text from scratch. It retrieves a set of candidate passages from a corpus and then re-ranks them to select the best passage. This approach allows RARR to generate more accurate and informative text than traditional language models, but it can require more time and resources to calculate.
These three implementations for RAG all have different strengths and weaknesses. While what’s used is likely a combination of all three and more, the idea remains that documents and knowledge graphs are searched and used with a language model to generate a response, and with Google’s strength in search, they’re more than qualified to use this paradigm to surface and personalize information.
The Threat of AI Overviews to Organic Search
As AI Overviews become faster and more refined, the likelihood of users clicking on traditional organic results is decreasing. Although there still has not been any official Search Console data, third-party reports indicate a decline in organic CTR, particularly for top-ranking results positioned below AI-generated answers.
AI-driven search is also becoming more conversational and personalized. Search engines are starting to consider a user’s past queries, preferences, and intent, delivering increasingly tailored answers. This shift complicates traditional SEO strategies, as ranking well for generic keywords may no longer guarantee traffic.
Google’s mission has always been to organize the world’s information and make it accessible. As users move away from simple keyword-based queries, their queries will get longer. Head terms will shrink while chunky middle and long-tail queries will grow.
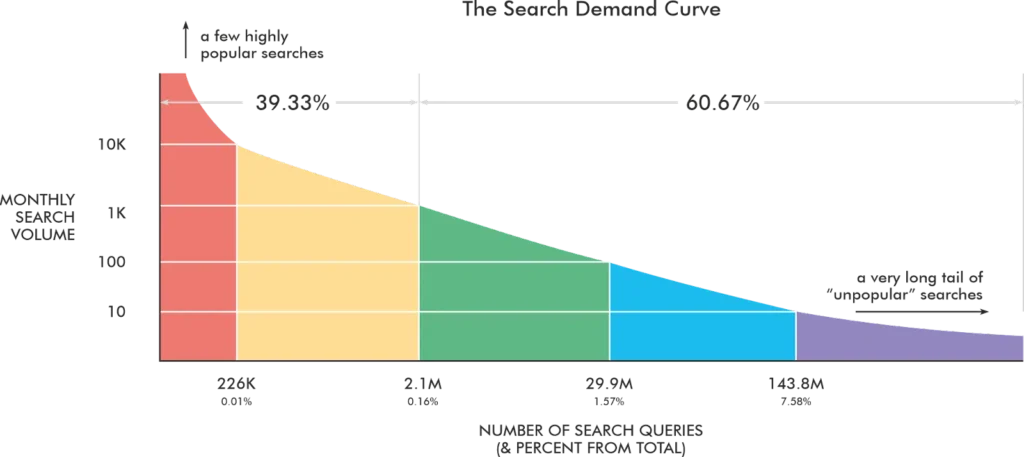
Follow-up questions will give users “Choose Your Own Adventure”-style search journeys, making searches multidimensional. This will force content creators to make content that fulfills multiple stages of these new journeys.
Adapting SEO for the RAG Era
To succeed in an AI-driven search landscape, SEOs must shift their strategies and ensure their brand, products, and content are structured in ways that AI can easily retrieve. Think of it as though you’re trying to get a featured snippet. Your content’s user experience should make it easy to find an answer.
- Focus on Entity-Based SEO: With AI search tools, you should focus on the semantic chunking of content. Shorter passages (50 to 150 words) improve retrieval accuracy because they focus on a single topic or idea. Also, use headings/subheadings to clearly separate sections.
- Leverage Fresh Content: If RAG retrieves the most relevant and current information, maintaining up-to-date content is essential.
- Track AI Overviews: Monitor how AI-driven search impacts rankings and visibility.
The Future of RAG and AI Mode
On March 5, 2025, Google introduced AI Mode, claiming it “expands what AI Overviews can do with more advanced reasoning, thinking, and multimodal capabilities so you can get help with even your toughest questions.” Though it’s still in experimental mode and not yet available to the general public (it’s available only as an opt-in through Labs), its potential impacts are already apparent.
It combines aspects of Google’s knowledge graphs as well as shopping graphs to provide the most up-to-date and customized search results. This development, introduced by Microsoft in 2024, is referred to as Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG). AI Mode also allows for follow-up questions for a more conversational approach to search queries.
AI Mode will also be multimodal, so it will be able to process your question through voice, text or images.
Google CEO Sundar Pichai wrote on X: “And just like AI Overviews, AI Mode will get better with time and feedback.” The question remains: Will AI-driven search become a better experience? Only time will tell.
The Future of SEO
RAG is redefining SEO by making search engines more context-aware and personalized. AI Overviews, GraphRAG, and real-time retrieval are transforming search behavior, reducing reliance on traditional click-based search results. To stay ahead, SEOs must adapt by embracing structured data, engineering content that’s optimized for AI-driven results, and preparing for an increasingly conversational search landscape.
The future of search isn’t just about ranking number one anymore – it’s about ensuring your content becomes part of the entire AI ecosystem.






