Watch the FREE AI Overviews Optimization webinar replay with me and Mike King.
Google Search is fundamentally changing. Marketers need to reframe the way they approach content strategy and search engine optimization. Generative AI is being incorporated into the search results now and nobody knows what that will mean for the future of search.
- Will we see a 90% decrease in organic traffic?
- Will AI completely replace traditional search results eventually?
- Is SEO dead? (I couldn’t help myself).
Search results have been evolving for decades, nothing surprising there. It’s morphed from 10 blue organic links into a completely bloated smattering of ads, rich snippets, navigation elements, verticalization features, personalization features, and a few organic results.
AI Overviews (previously SGE) is Google’s crescendo, the next phase, and its biggest gamble.
We’ve got so many questions:
- What’s Google’s vision for the future of search?
- How will AI change search behavior?
- What can marketers do to prepare?
- What other bigger implications need to be considered?
Google’s never fully transparent. So let’s read between the lines, tease out some possibilities, and leave you with some things to consider.
Table of Contents
What is the AI Overview (SGE)?
The AI Overview is Google’s AI-powered snapshot that appears at the top of some search results. It consists of an AI Overview, generated text with sourced citations that provide a direct answer to the query. It sometimes includes additional context.
Below the AI Overview are follow-up questions. We also have some different layouts depending on the verticals (specifically ecommerce and local searches).
In February, I explained my personal take on AI Overviews on the Crowd Content webinar:
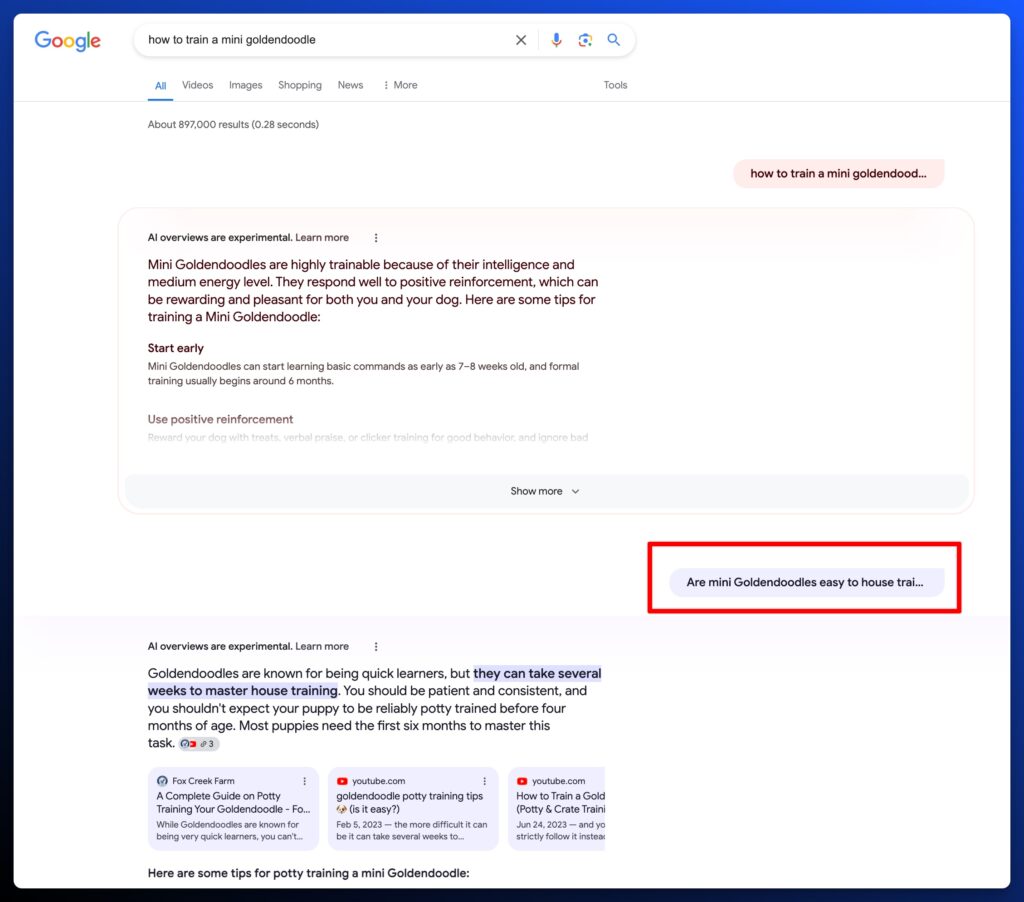
Take a look at what a ‘current’ version of AI Overviews looks like. This example includes a variety of output formats:

Depending on the query, the layout potentially includes a variety of formats:
- Paragraphs (sometimes with images)
- Bulleted lists
- Breakouts (A series of sub-headers and short paragraphs, sometimes accompanied by images.)
- Images
- Videos
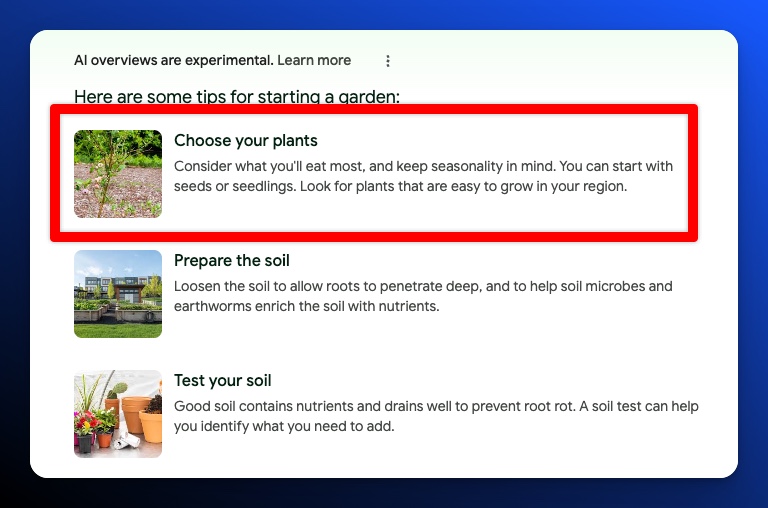
Despite the additional context, you will typically see the most relevant part of the answer highlighted:
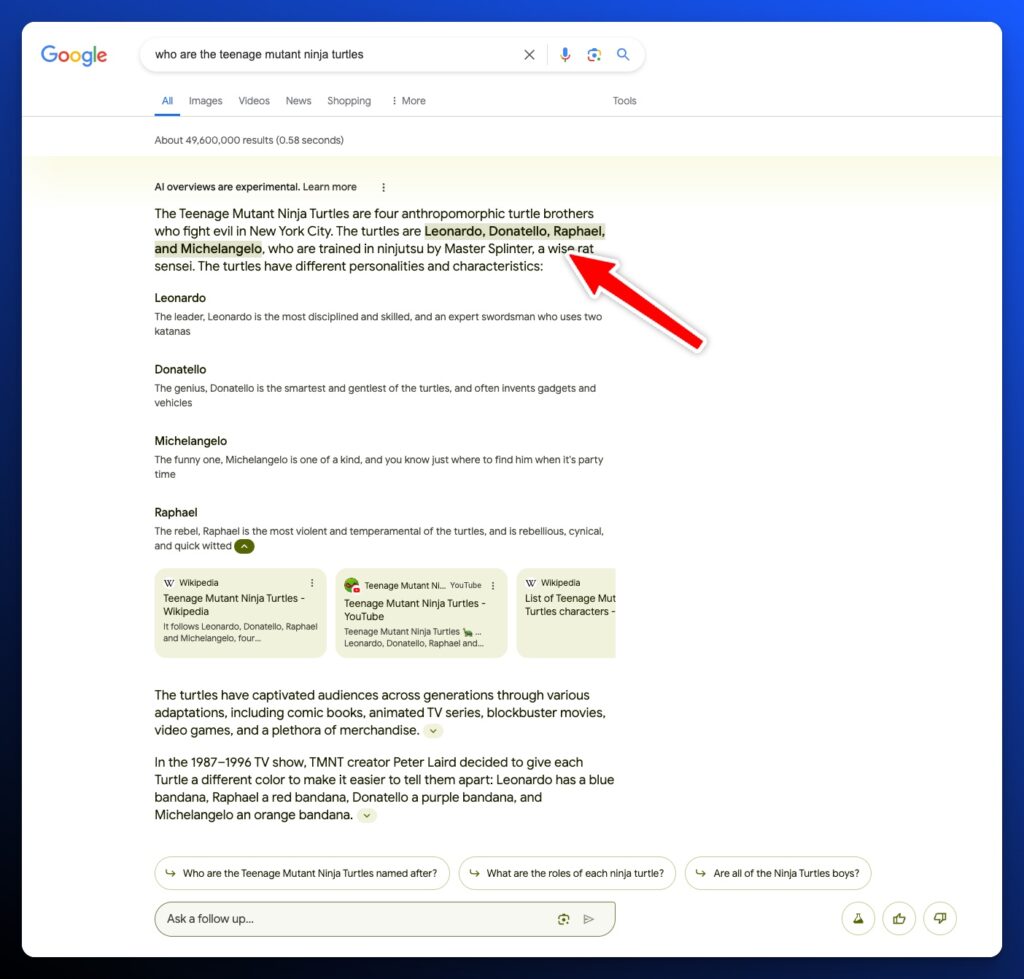
Every text element has citations of its sources.
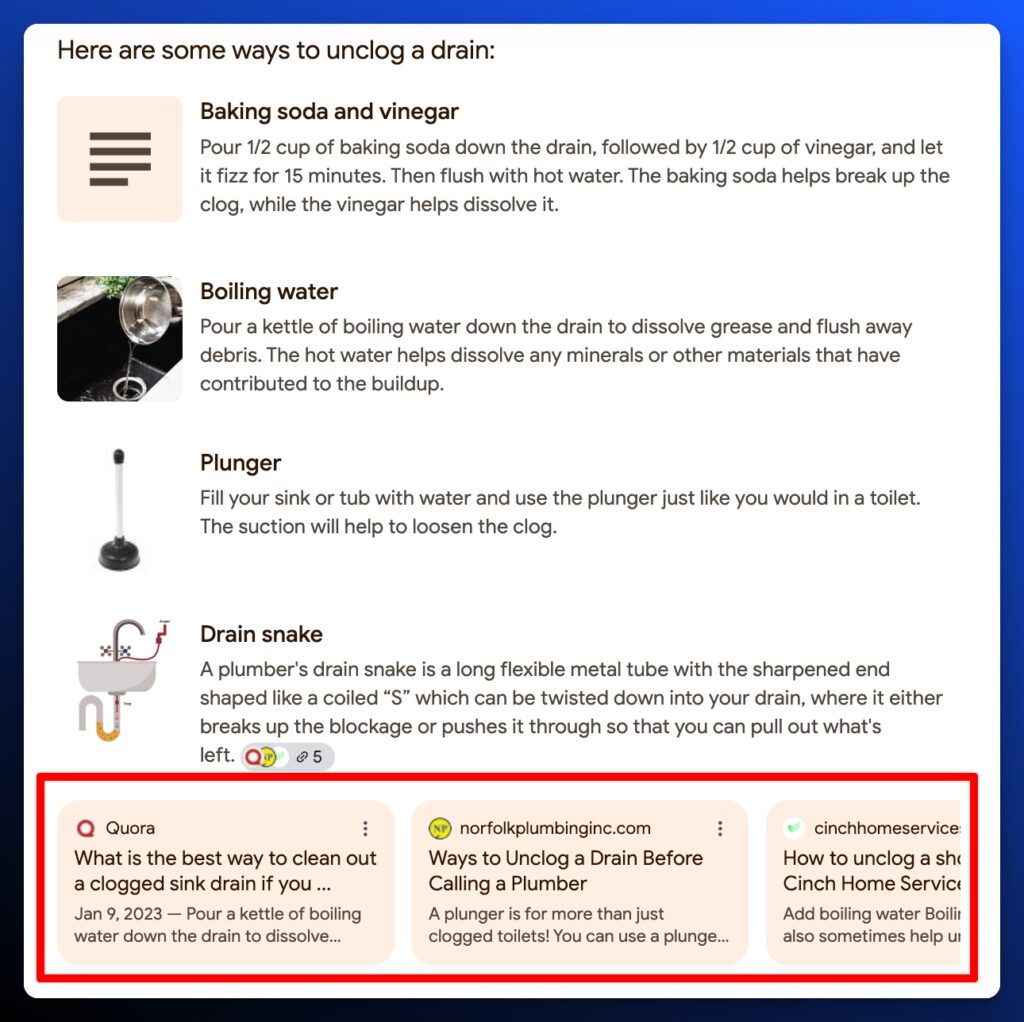
Most recently, the citation dropdown has been populated by favicons from the sources.
A carousel of sources appears to the right of the AI Overview that typically includes an image, article title, date, and website name (which is a clickable link), though the carousel has been removed.
Below the AI Overview, we sees 2-3 follow-up questions that are relevant to the original query. Those follow-ups are typically different from Google’s People Also Ask feature further down the Search Results Page.
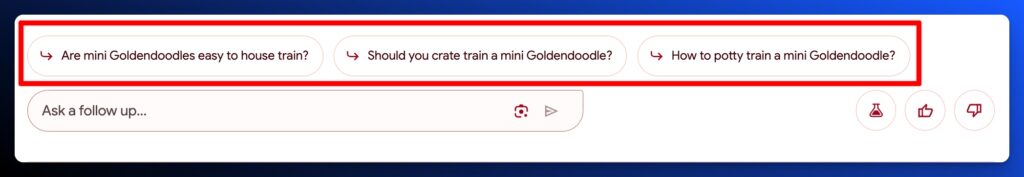
And when you click on the follow up, AI Overviews keep the conversation contextual.
Note: The design, labels, elements, and even the name of AI Overviews are constantly changing. A few tests include:
- The aforementioned citation favicons.
- Recently, the carousel has been completely removed.
- The label at the top of the AI Overview previously only stated that ‘Generative AI is experimental.’
- Citations were originally hidden in a collapsed section, revealed by a bear claw option.
SGE also includes two different layouts unique to shopping queries and local queries.
For a commercial search, you’re likely to see a list of products that are sourced from product review articles or Google’s Shopping Graph in a few different formats:
Standard Product List
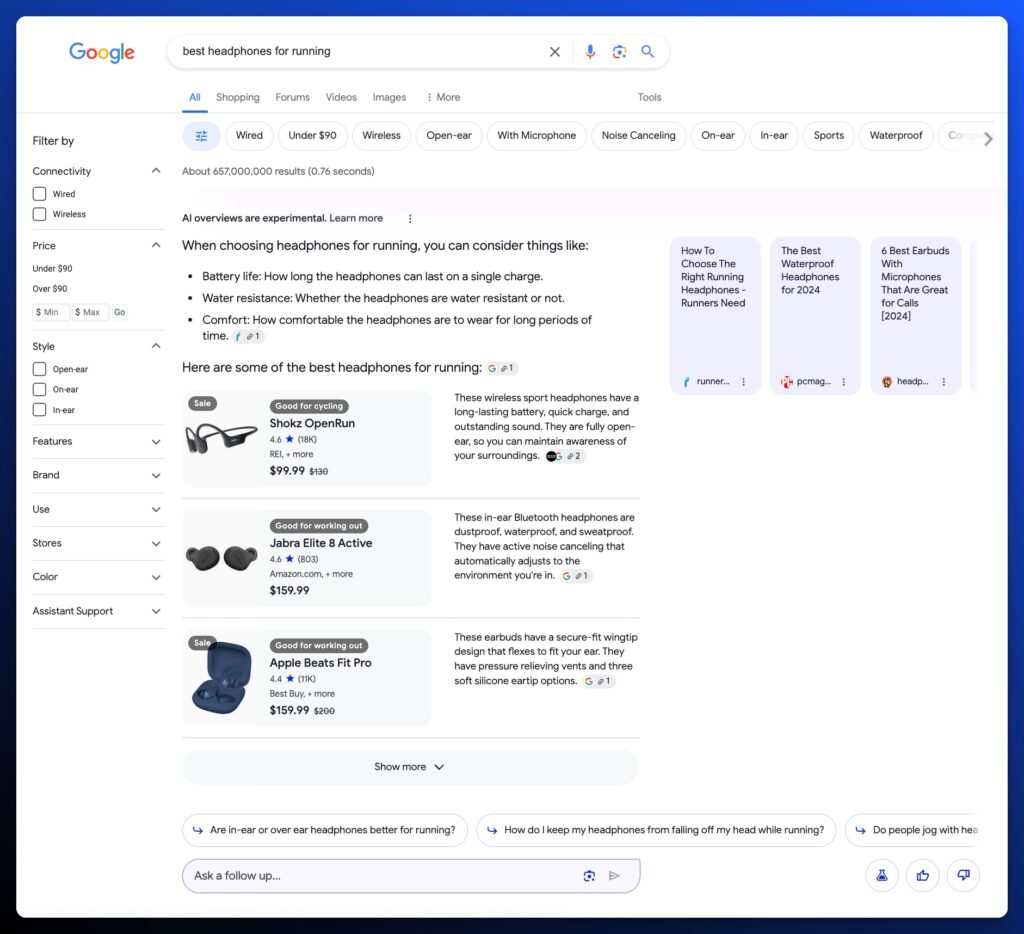
eCommerce Grids
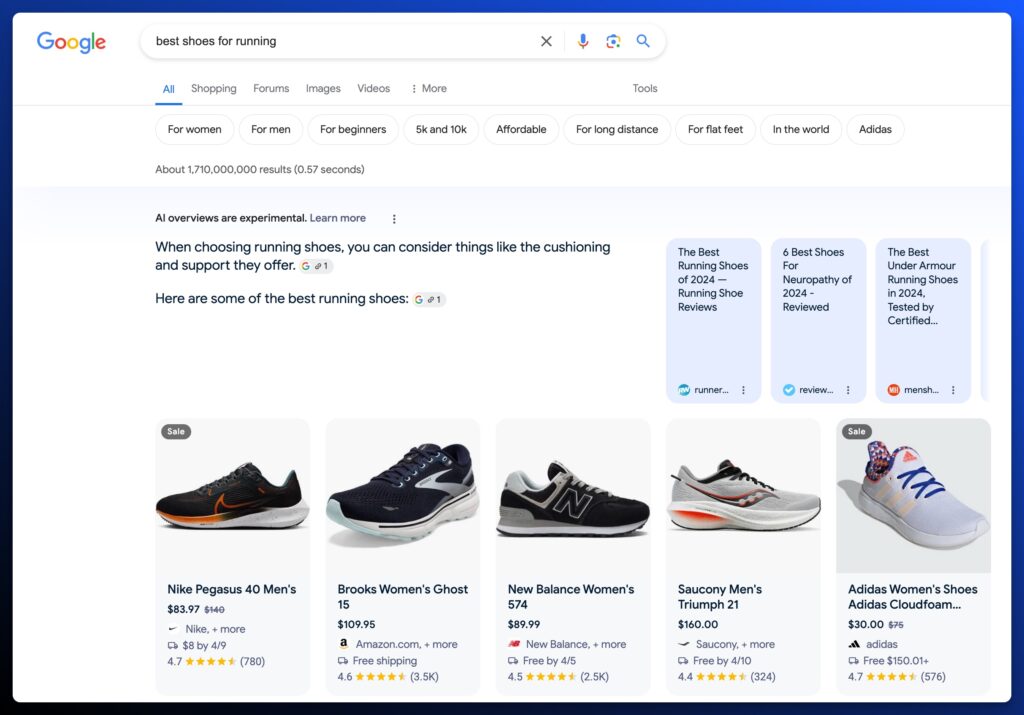
Categorized Compilation Packs
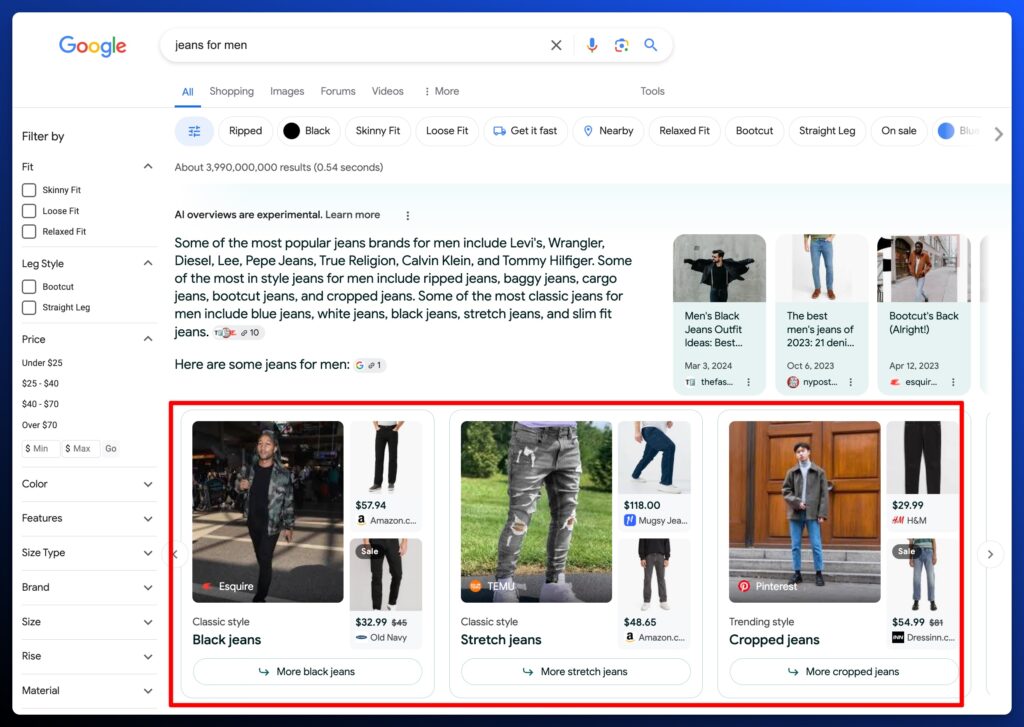
The eCommerce results have significant implications. If searchers use AI Overviews for product selections, then it’s essential that brands make sure that they have invested resources in optimizing their products in Google’s Shopping Graph.
Local searches that are based on your geography have a unique layout as well. They typically include the map pack, citations, and a carousel above the map pack. They also include labels for business attributes.
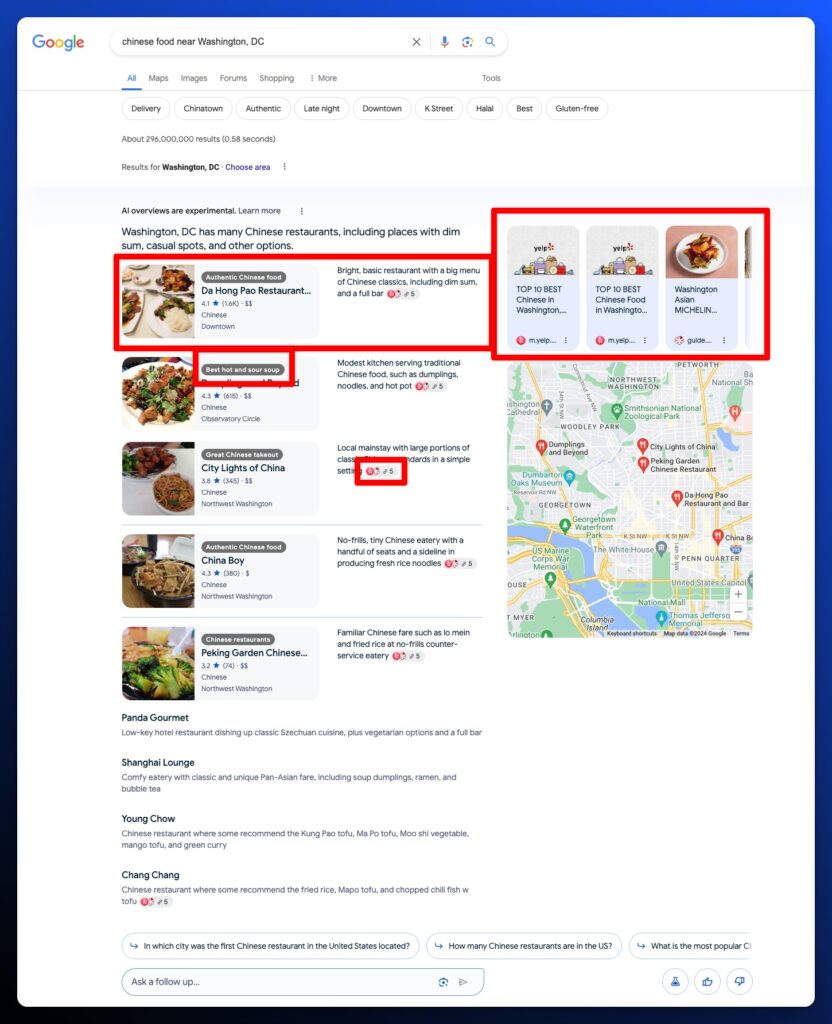
The biggest unanswered question for AI Overviews is what role will Ads play. Up to this point, we’ve seen ads appear directly above and below the snapshot, but not inside of it. Considering the importance of ad revenue, it feels inevitable that ads would be integrated into AI Overviews in some capacity. Google has indicated that they will continue to experiment with ads. According to CEO Sundar Pichai during Alphabet’s Q4 earnings call:
“As we shared last quarter, ads will continue to play an important role in the new search experience and will continue to experiment with new formats native to SGE. SGE is creating new opportunities for us to improve commercial journeys for people by showing relevant ads alongside search results. We’ve also found that people are finding ads either above or below the AI-powered overview helpful as they provide useful options for people to take action and connect with businesses.”
As important as the content, visual design, and inclusion of ads are to the success of SGE, its visibility and timing in search results are just as critical for SEOs.
UPDATE (Hours later): The paint has yet to dry on this article and hours later, news leaks that Google is considering a paid GenAI (and potentially AI Overviews) product.
It is unclear how exactly the company would seek to integrate AI-powered search into these paid-for services, which offer different pricing tiers, or when the AI-powered search offering would be ready to launch. Google could still decide to launch certain elements of its experimental AI-powered service into its main, free search engine over time, according to people familiar with its thinking. Google said the company was “not working on or considering” an ad-free search experience but that it would “continue to build new premium capabilities and services to enhance our subscription offerings across Google”.
While this article doesn’t explicitly claim that Google will only use AI Overviews as a paid feature, it will be an interesting situation monitor considering that Google has rarely added paid features like these to its free products.
One reasonable concern for this business move would be the cost to run AI Overviews along with the risk to Google’s ad model.
If searchers are less likely to click on ads due to AI Overviews’ ability to satisfy user intent without leaving the search results, then that would require another way to monetize AI Overviews.
When Does AI Overviews Trigger?
The AI Overview does not appear for every search. There are five scenarios for any given query:
- Automatically generated at the top of the search results page.
- A truncated automatically generated at the top of the search results page that needs to be expanded.
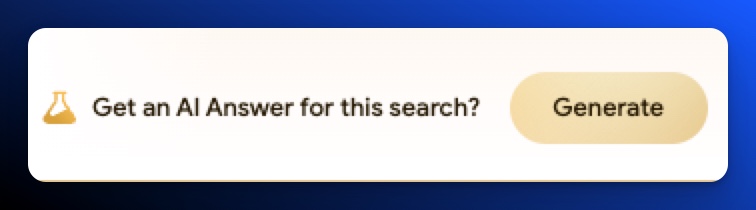
- A message to “Get an AI-powered overview for this search?” with a Generate button to click.
- A message that “An AI-powered overview is not available for this search.”
- No indication of an AI-powered presence.
Update 4/28: Google has softened the copy for your average user with “Get an AI Answer for this search?”
Further down in my coverage of AI Overviews research, you’ll see the frequency of AI Overviews’ appearance along with which industries are likely to see the feature most. That’s an important consideration since Google’s been adamant about responsibly bringing AI to search.
The Philosophy Behind AI Overviews
Google’s AI Overviews team published a 16-page SGE Overview back in May 2023 that reads like a manifesto.
Everyone working in SEO should read the overview. It’s chock full of goals, philosophies, and intentions for the future of AI Overviews.
Fundamentally, “SGE is an early step in transforming the Search experience with generative AI.”
An early step, but the first of many.
The blueprint paints a picture of the responsible implementation of generative AI search:
“When using SGE, people will notice their search results page with familiar web results, organized in a new way to help them get more from a single search. With generative AI in Search, people are able to:
- Ask new kinds of questions that are more complex and more descriptive
- Get the gist of a topic faster, with links to relevant results to explore further
- Get started on something you need to do quickly, like writing drafts or generating imagery right from where you’re searching
- Make progress easily, by asking conversational follow-ups or trying suggested next steps”
Naturally, Google wants AI Overviews to be a better search experience. They want you to find more helpful information without needing to pogo-stick between websites and back to search.
And AI Overviews will play a big role in the future of search. Recently promoted Head of Search Liz Reid shared her excitement for the experiment on LinkedIn in March.
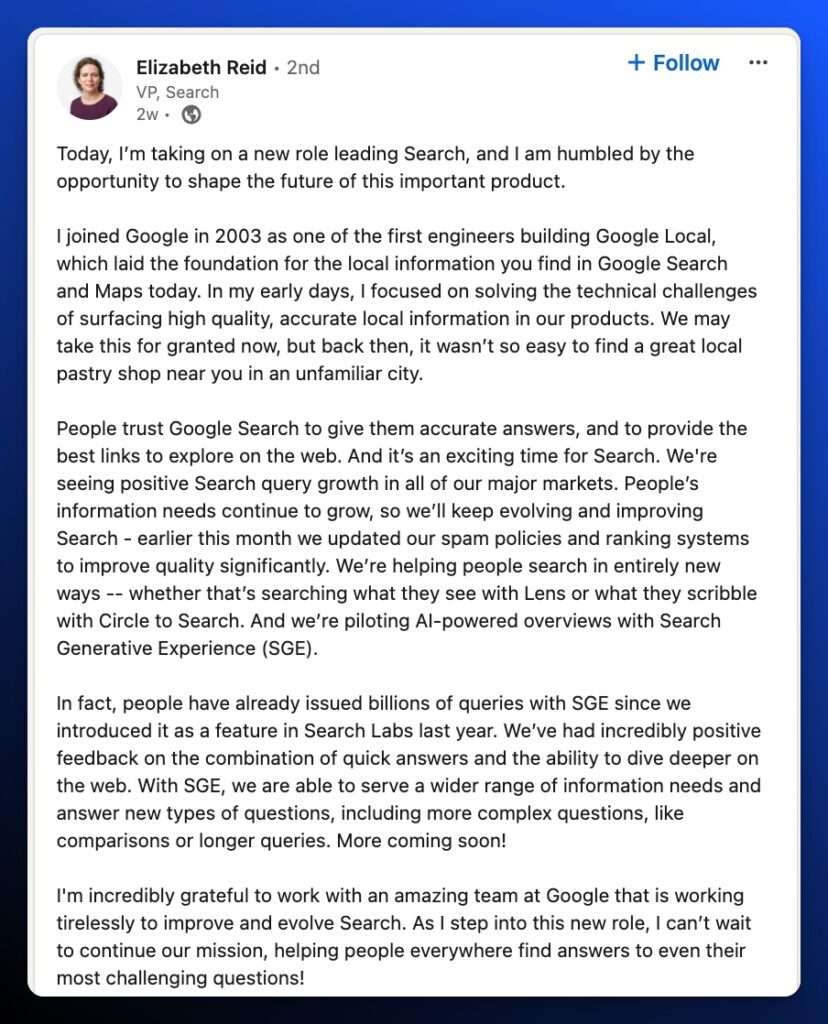
Considering Liz’s role in bringing AI to search, Google is telegraphing their plans here.
And the move makes sense from Google’s perspective. It’s not the first time they’ve aimed to keep searchers on Google. Despite all of their talk about building a healthy web, the more time spent on the search results, the more ad impressions, the more ad revenue.
Featured snippets have been around since 2014. For the most simple definitions or simple answers, pulling a word-for-word passage from a web page saved searchers a ton of time.
Truthfully, most people want the cliff notes most of the time. We don’t want the story behind the recipe (unless we do). We don’t care about the history of your nomadic life to learn about the best things to do in Jamaica (unless we do.)
For informational searches with one answer, we don’t always need the *best* info. Information can be commodified.
We need info that’s good enough (or Goog enough). We expect it to be accurate. AI Overviews aims to reduce the work to discover answers and solutions. Reduce the cognitive load. We’re satisficing our search results. We want the TL;DR. If we like the person, brand, or writing, we’ll put in the work to read more. We have the option.
But the LLMs have their known limitations:
- Hallucinations: They still make things up.
- Misinterpretations: Despite significant gains in Natural Language Processing, it still doesn’t understand the nuance of every query.
- Bias output: The outputs are still trained on biased content and the internet is full of biased content.
- Persona corruption: Sometimes the output will have an opinion despite Google’s engineer’s guidelines to reflect a neutral and objective tone.
The team at Google claimed that they were going to limit the use of AI Overviews for critical queries that are financial-related or health-related(Your Money Your Life or YMYL). But early on in experimenting, YMYL searches frequently had results.
It’s in Google’s best interest for AI Overviews to produce helpful and safe results. If the AI Overview consistently creates snapshots that are deceptive, unsafe, or worse than the traditional search results, searchers will begin to look elsewhere for their information. Fewer searches mean less ad revenue: Alphabet’s primary source of revenue.
To that end, the overview claims that they have a few key processes in place to monitor, review, and evaluate performance of the feature:
- Raters: We work with independent Search Quality Raters to help us measure the quality of outputs and the results displayed. These ratings do not directly impact SGE’s output, but are used to train the LLMs and improve the experience overall.
- Focused analysis: Following our process for significant launches in Search today, we analyze results across multiple broad, representative query sets, as well as conduct more focused studies to confirm responses meet our quality thresholds. In particular, we focus on topic areas that may be more susceptible to known quality risks, or that are more complex and nuanced. This includes classes of queries that may be at higher risk for safety or inclusion issues and aims to ensure our protections and responses are effective across those domains.
- Red-teaming: We conduct adversarial testing of these systems to identify areas where the systems aren’t performing as intended. This helps identify bias issues, safety concerns and other areas where we can improve the product.
With both CEO Sundar Pichai and Head of Search Liz Reid claiming that people ‘love’ SGE, it’s difficult to determine whether this is heavy-lifting PR or based on testing, feedback, and results.
“We are incorporating SGE in the product, the early feedback is positive…And we’ve been iterating on it, and it clearly works for certain types of queries very well. We are expanding the set of queries where it works very well. It definitely is answering a certain category of queries for the first time in a better way. So that gives us direction to proceed as well.”
The next phase will be seeing these results in public. As SEOs, it can be very difficult to step outside of our niche, our bubble, our industry, and see the search experience from the perspective of everyday users.
But the quality of the results depends on the technology in place.
So what’s the actual (virtual) machinery behind AI Overviews?
How Do AI Overviews Work?
Powered by a variety of Large Language Models, including an advanced version of MUM and PaLM2. it generates text from relevant content across Google’s Index.
You cannot confidently claim to know the exact tech behind what makes AI Overviews (or any of Google’s Search products run). But you can turn on your inner detective and sus out the patents, frameworks, processes, costs, and resources, that would theoretically drive the feature. Unfortunately, you can’t always trust Google employees or press releases to truthfully reveal their IP.
So what can we infer?
Juan Gonzales Villa identified the likely Google Patent (granted in September 2023) for an AI Overviews process. What’s interesting is that it shows how AI Overviews could use one or multiple LLMs for the generated text. It also can use additional systems or skip them depending on the needs of the query.
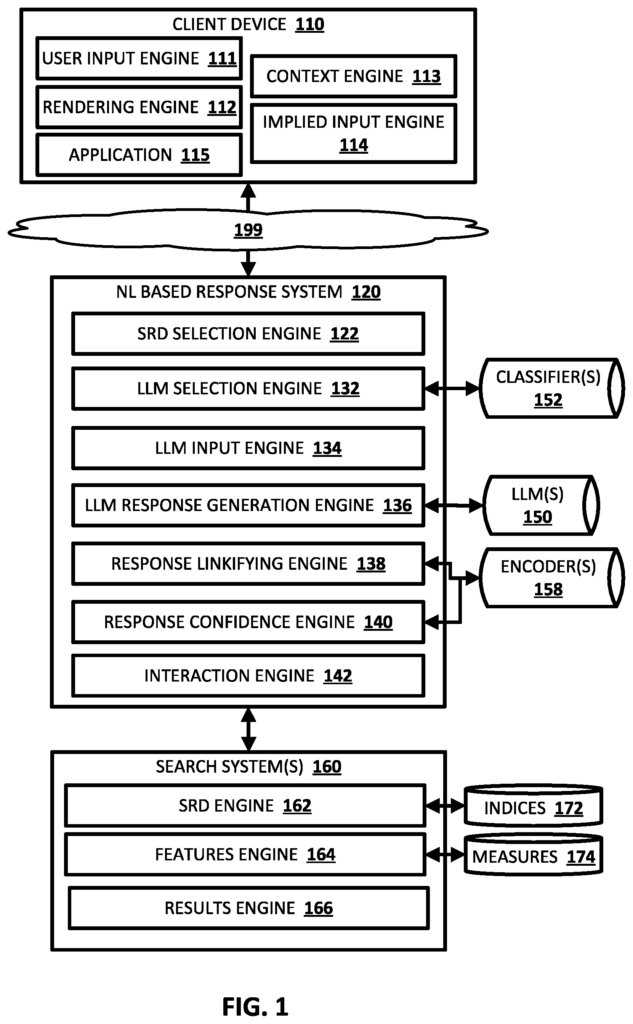
Instead of being trained purely on a static dataset, AI Overviews uses a process called Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to use current content in its output. Fresh, up-to-date information from websites.
Google takes the query, generates an AI summary from relevant content on the web, evaluates the summary, rewrites it, and then annotates it with a graded level of confidence.
Here’s a simplified visualization of the process for Google’s Index, Knowledge Graph, and LLM.
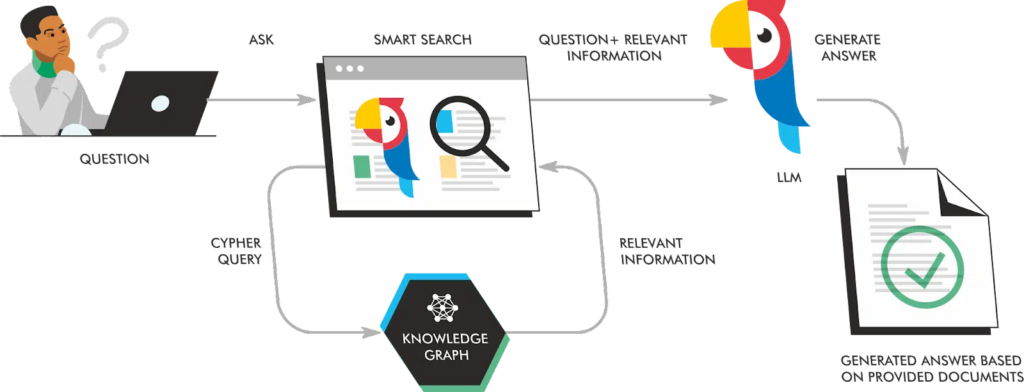
For a comprehensive technical deep dive, read How Search Generative Experience works and why retrieval-augmented generation is our future by Michael King.
Mike reveals how AI Overviews produces generated output from chunks of relevant content that can be quantitatively calculated.
You can then use a tool like MarketBrew’s SGE Visualizer to evaluate whether your content has a high enough similarity score that it would potentially be included in AI Overviews.
I broke this down in my AI Overviews optimization article.
The technology continues to evolve and much of it is hidden in the Google blackbox where nobody can tell you exactly how it works.
According to the AI Overview referenced earlier:
“While SGE also applies LLMs, it has been purposefully trained to carry out tasks specific to Search, including identifying high-quality web results that corroborate the information presented in the output. These models are used in tandem with our core ranking systems to deliver helpful and reliable results.”
Personally, I’m skeptical that the algorithms and systems used by AI Overviews are the same used for core search. We’ll address this a bit more in the analysis section below, but the sources for AI Overviews output rarely primarily pull from the top few organic search results.
Cindy Krum has proposed some interesting theories around how Google uses systems (Spam and Helpful Content Systems) to filter out bad data and keep the generated output clean.
This would support Google’s desire to create AI-enabled products responsibly.
The Timeline Behind the Search Generative Experience and AI Overviews
A quick timeline of AI Overviews for the uninitiated. Google is always evolving its search results. If you want to dive into everything Google has implemented over the past couple of decades, consume How Search Works. Collecting and organizing the world’s information and making it accessible to everyone is an impossible responsibility, but they’re the best at it.
That said, Google Search has earned deserved criticism.
In January of 2022, we started to see a series of thought pieces bemoaning that Google Search Results were disappointing. Michael Seibel, Managing Director at YCombinator tweeted a scathing Twitter thread,
Health, product reviews, recipes are three categories I searched today where top results featured clickbait sites riddled with crappy ads. I’m sure there are many more. Feel free to reply to the thread with the categories where you no longer trust Google Search results.
— Michael Seibel (@mwseibel) January 2, 2022
The replies echoed his experience. More people were turning to Reddit and TikTok for searches and that became a common theme throughout 2022.
people are now searching on tiktok instead of google pic.twitter.com/YTbH3Ap65t
— Turner Novak 🍌🧢 (@TurnerNovak) June 21, 2022
In late 2022, ChatGPT enters the chat. All of a sudden generative AI appears to be a search competitor. However, many SEOs and Large Language Model experts caution that the tool has critical limitations for search.
- GPT-4 was originally trained on content from before 2021, it’s since been updated on its training data as recently as April 2023.
- LLMs are biased by training data providing harmful results.
- It often produces factually inaccurate results (sophisticated predictive text).
Despite these elements that make ChatGPT problematic as a search engine, in January 2023, Microsoft announced a multi-billion dollar investment in OpenAI, paving the way for an integration with the tech giant’s own search engine Bing. The rollout was quick and not without glitches and hitches.
Google had been building toward a generative AI product all along. According to the New York Times, in April it was revealed Microsoft was on the verge of a potential business deal with Samsung to replace Google Search with Bing as the homepage of Samsung’s devices.
Murmurs in the media indicated that something was coming, but we initially didn’t know if it would be a stand-alone chat (which turned out to be Gemini) or an integrated generative AI search that turned out to be the Search Generative Experience (announced in early May at Google I/O).
Weeks later, the AI Overviews Experiment was opened up and SEOs began playing with the new AI Snapshot interface.
When the December 2023 experiment ended, SEOs were skeptical that AI Overviews would ever make it into production.
In March, the 2024 Core Update and Spam Update stole headlines by integrating the Helpful Content System, devastating a range of niche sites, while independently, manual penalties were being levied on high-profile generative AI content sites.
Meanwhile, in late March, Google began to test AI Overviews in the wild.
To see AI Overviews publicly tested despite still generating some questionable (even problematic) results was an unexpected move by Google. The same company that has maintained a culture of extremely high standards and AI responsibility.
And if you laugh at that sentiment, watch their 2020 documentary Trillions of Questions, No Easy Answers. They have a rigorous production process that appears more cutthroat than a Ph.D. defending her dissertation.
Update, on May 14th, 2024 at Google I/O, the team announced the AI Overviews rebranding and a variety of new features including:
The Search Generative Experience has been rebranded as AI Overviews and will launch immediately.
AI Overviews uses:
• Real-time info (knowledge graph)
• Algorithmic Systems
• Customize Gemini for Search
AI Overviews can understand:
Multi-step reasoning in Google search: Ask multiple questions at the same time and conduct planning. (Meal Planning, Itineraries, Events)
Ex. Search for location with multiple criteria all at the same time.
A new AI-Organized Search Results Page:
• Clusters of results.
• Contextual Factors.
• Rolling out when you look for inspiration (dining, recipes, books, etc.)
WHOA. Ask with video. That’s intriguing.
Gemini and Search figures out the video frame by frame. Stitches it together in AI-organized result.
Check out the video.
So with Google definitively moving forward with AI Overviews, what’s the big motivation behind AI in search?
Current AI Overviews Research and Analysis
As SEOs, we’re desperate to get a handle on the implications of AI Overviews. The implications of AI Overviews across search results could have an even greater impact than featured snippets. We need to prepare for a decline in organic search traffic that comes from our traditional blue links and strategize ways that our content can appear in the AI overview and drive either organic traffic or brand awareness.
There have already been a series of studies that have investigated a few pertinent questions for AI Overviews:
- When do AI Overviews trigger?
- Where do AI Overviews get its sources from?
- How are different verticals impacted?
- How long does it take for AI Overviews to load?
To get a custom report on the potential impact of AI Overviews on your organic search traffic, sign up for the SGE Threat Report.
Keeping in mind that AI Overviews constantly experiments and evolves, here are the current reports on AI Overviews’ impact in chronological order:
How SGE will affect your SEO and business - Bartosz Góralewicz
Date: 8/9/23
Queries Analyzed: Undisclosed
Key Takeaways:
- SGE results were available for 81% of queries in our database.
- 85% of sources quoted in SGE results rank within the top 10 positions
- eCommerce queries seem to be Google’s core focus, with a staggering 92% coverage as of July 30th, 2023
- Finance-related queries from our database are only covered in 24% of cases
- Google’s SGE targets 87% of medical/health-related queries we track in our database
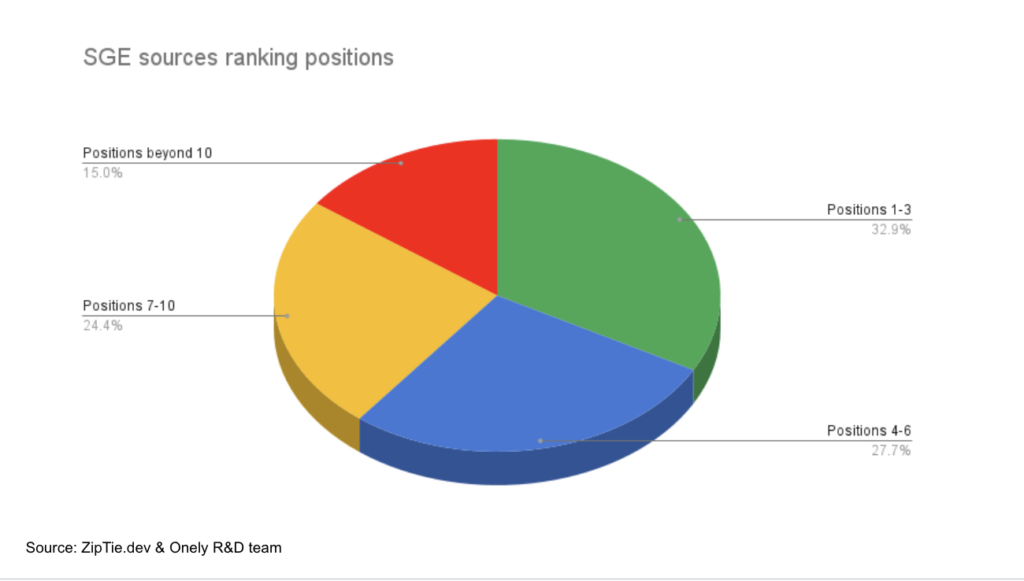
My Take: Bartosz provides insights into specific verticals with his study. Despite the undisclosed number of keywords used for his analysis, it’s still shocking to see that Google targeted 87% of health-related searches. Considering that at Google I/O in 2023, they hedged that they would take a responsible approach to SGE and that SGE still hallucinates, you’d think we wouldn’t see so many snapshots for important YMYL searches.
How Search Generative Experience works and why retrieval-augmented generation is our future - Mike King - iPullrank & Search Engine Land
Date: 10/19/23
Queries Analyzed: 91,000
Key Takeaways:
- AI snapshots originally took an average of 6.08 seconds to generate. Over the past few weeks, we’ve seen the average SGE result generated in less than a second.
- 60.34% of queries did not feature an AI snapshot.
- Positions 1, 2, and 9 get cited the most in the AI snapshot’s carousel.
- 9.48% of the time, SGE does not use any of the top 10 results in the AI snapshot.
- SGE is auto-triggered on 58% of News/Media Queries, 35% of eCommerce clothing queries, and 78% of banking queries.
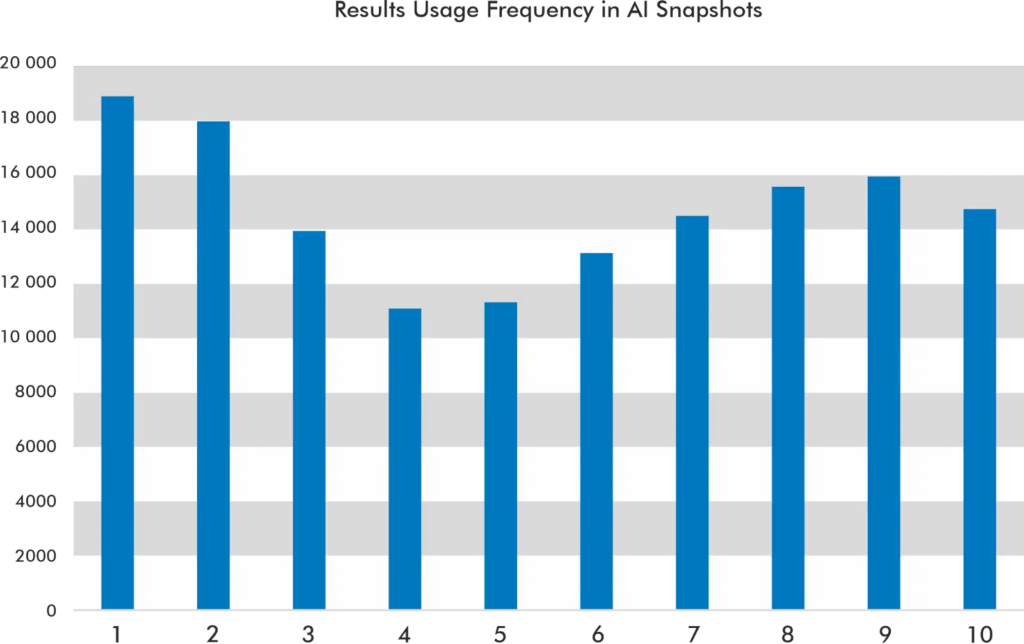
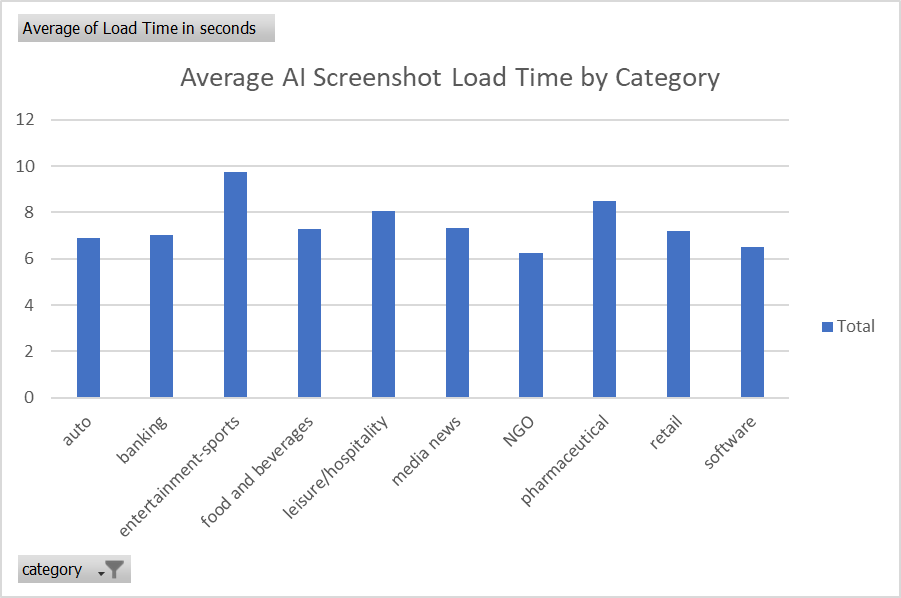
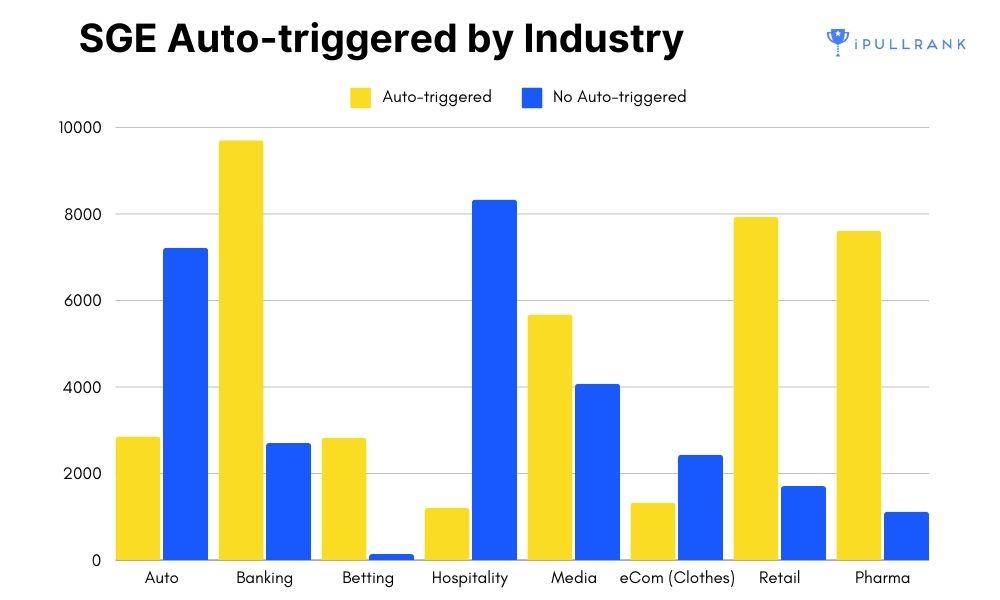
My Take: Mike’s research includes one of the largest sets of keywords. The fascinating part of his focus was on the impact of SGE’s load times. If the feature takes too long to load, people are going to ignore it. Google seems to be improving the speed of SGE, but that comes with a cost. One of the underlying subplots with SGE’s implementation involves the potential cost to run it for most queries. It’s expensive. More expensive than a normal search result.
Research Study - The Impact of Google's Search Generative Experience on organic rankings - Laurence O’Toole - Authoritas
Date: 1/4/24
Queries Analyzed: 1000 Keywords
Key Takeaways:
- Google displays a Search Generative element for 86.8% of all search queries.
- 65.9% of the time a small generate button appears but 34.1% of the time a pre-populated SGE element appears with a ‘Show More’ link.
- When a user clicks on the SGE button or the ‘Show More’ link, then the No.1 organic listing shifts down the page by 1,562 pixels and 1,630 pixels respectively. This is ~1.5 times the height of the viewport and therefore it’s inconceivable that this won’t impact click-thru rates and organic traffic.
- On average there are 10.2 links in the SGE content post-click from 4 unique domains.
- The largest generative content introduced 37 new visible URLs above the organic rankings!
- 93.8% of generative links (in this dataset at least) came from sources outside the top-ranking organic domains. With only 4.5% of generative URLs directly matching a page 1 organic URL and only 1.6% showing a different URL from the same organic ranking domain.
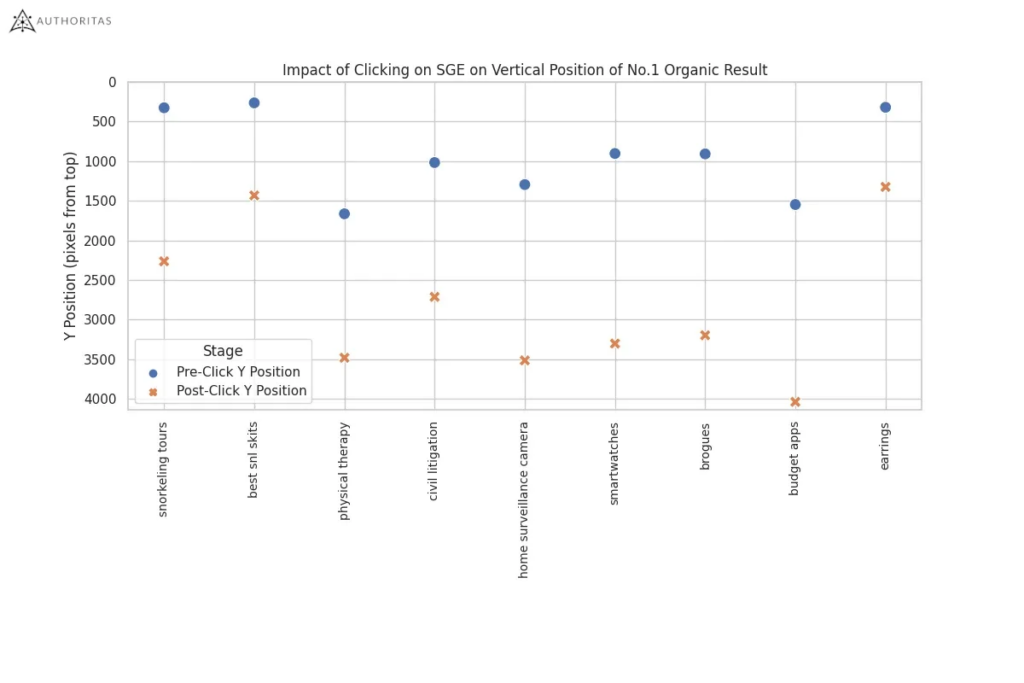
My take: In this first study by Laurence, I love the specific look at the pixel depth of SGE. It’s been a consistent callout among SEOs that organic search results are pushed further and further down the viewport as Google increases the number of ads and other features. Things are even worse on mobile. While we’ve seen a truncated version of SGE recently, if people click on it, there’s a good chance they’ll never get to the traditional organic results.
A Searchquake is coming! - BrightEdge
Date: 1/18/24
Queries Analyzed:1 Billion keywords
Key Takeaways:
- Google’s Search Generative Experience is poised to affect over $40 billion per year in ad revenue on Google.
- 84% of search queries will include Gen AI.
- Healthcare: 76% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Ecommerce: 49% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- B2B Tech: 48% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Insurance: 45% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Education: 44% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Restaurants: 36% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Entertainment: 36% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Travel: 30% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
- Finance: 17% of queries analyzed were impacted by SGE.
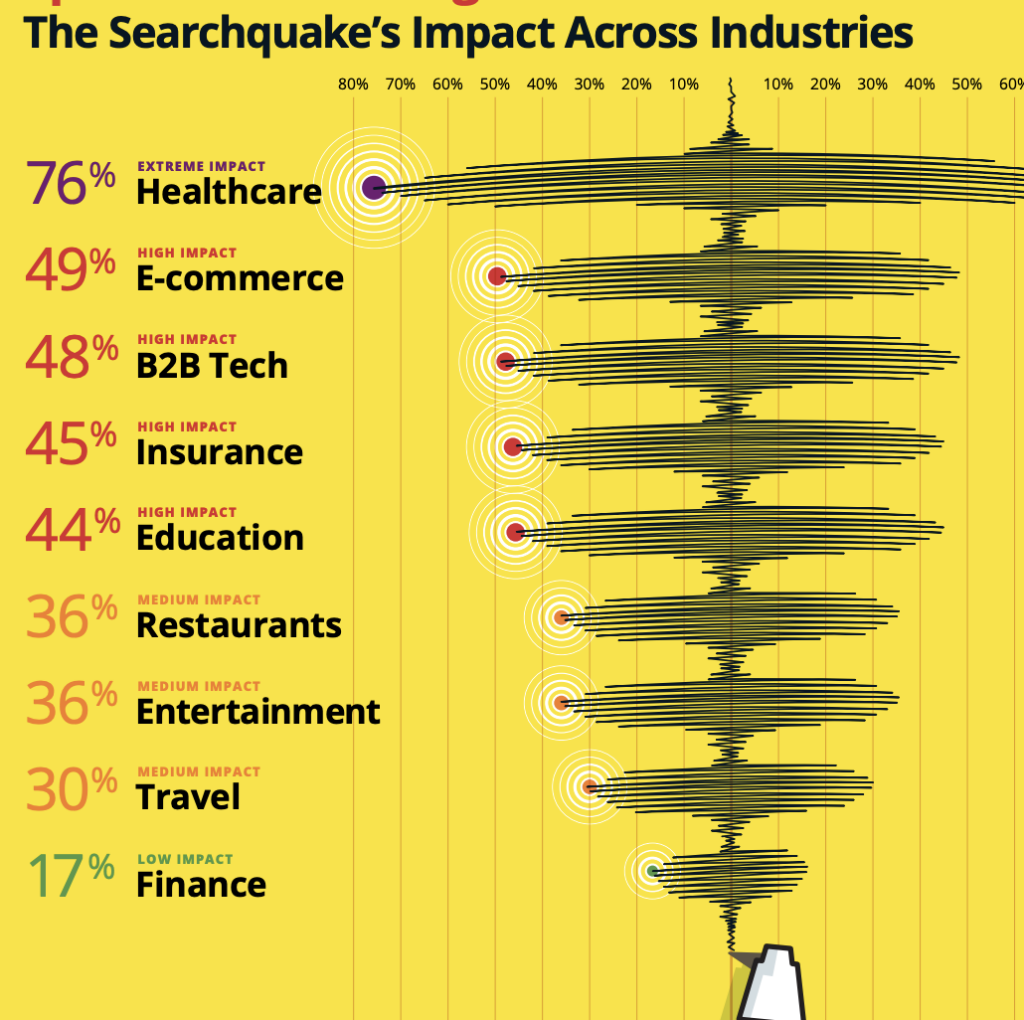
My Take: BrightEdge’s research is hard to swallow, but for such a massive enterprise, looking at 1 billion keywords can’t be dismissed offhand. The $40 billion impact is eye-popping despite there not being any methodology to back up such a claim. Regardless, while skeptical, it’s clear that SGE could disrupt the ROI of organic search. One consideration to keep in mind is that a great deal of that impact could be a ‘reshuffling’ of the cards. For every change to the eCommerce search results, consumers might just end up choosing a different organic path to purchase.
SGE Research Study - The Impact of Google Search Generative Experience on Brand and Product Terms - Laurence O'Toole - Authoritas
Date: 3/21/24
Queries Analyzed: 2,900 keywords
Key Takeaways:
- Google displays a Search Generative element for 91.4% of all search queries (this was 86.8% when we looked at eCommerce terms in January).
- The lowest SGE penetration scores were in YMYL (Your Money – Your Life) verticals like Insurance (52%), Finance (71%), Professional Services (83%) and Health & Wellness (87%).
- Quora.com finished in the top 20 performing generative domains in 11 of 15 categories. The only categories where it failed to make the top 20 were Automotive and YMYL categories such as Legal, Insurance and Finance.
- When a user clicks on the SGE button or the ‘Show More’ link, the No.1 organic listing drops down the page by an average 1,255 pixels.
- The No.1 Organic drop varies from a high of 1,723 pixels in Office Supplies and 1,718 in Fashion & Apparel to a low of 572 in Insurance – our Wave 1 eCommerce research showed a drop of ~1,500 pixels and both studies reflect a huge change in the SERP for product related queries.
- On average there are 10.75 links in the SGE content post-click from an average of 4.3 unique domains.
- 62% of generative links (in this dataset at least) came from sources outside the top 10 ranking organic domains. With only 20.1% of generative URLs directly matching a page 1 organic URL and only 17.9% showing a different URL from the same organic ranking domain. This is much better than the 93.8% reported in our eCommerce study.
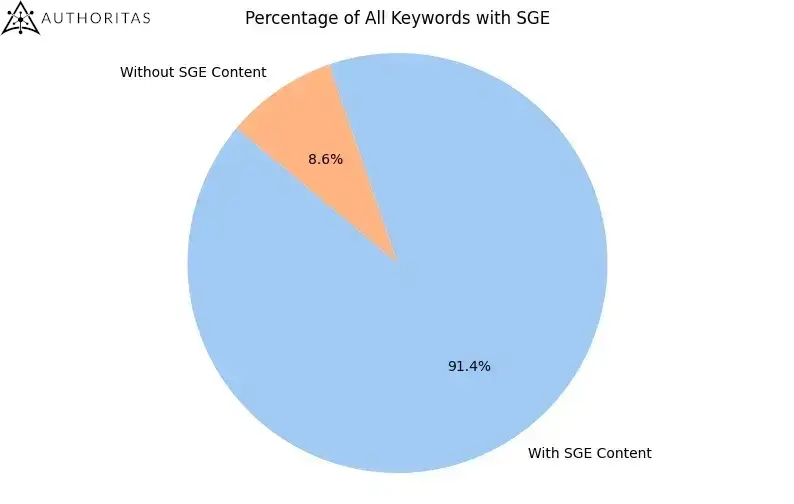
My take: Laurence found the strongest evidence that organic search traffic will be threatened by SGE. With 91.4% of queries resulting in a snapshot, no websites are safe. The big question will be whether actual users find these answers helpful enough. Commercial intent queries will still drive traffic since you can’t buy products through Google (yet), but simple informational content is at risk.
SGE Snippet Research: We Analyzed 100K Keywords to See Google’s AI in Action - Yevheniia Khromova - SE Rankings
Date: 2/26/24
Queries Analyzed: 100,000 Keywords
Key Takeaways:
- 64% of the analyzed keywords either have an SGE answer or a Generate button.
- Average text length of the SGE snippet: 3,485 characters.
- Sources: SGE most frequently has 8 links.
- 85.5% of SGE snippets link to one or more domains from the top 10 organic results.
- Most linked domains in SGE:
- quora.com,
- local.google.com (Google Maps),
- en.wikipedia.org
- Keywords from the Food and Beverage niche trigger SGE snippets most often, while the News and Politics niche gets SGE responses less often.
- SGE snippets containing text appear in SERPs alongside featured snippets approximately 25% of the time.
- Ads were present above or below SGE 73% of the time. 27% No ads.
- Ads at the top of the SERP accompany SGE snippets more often than shopping ads, but shopping ads tend to appear above the SGE snippet.
Industries most likely to get a snippet:
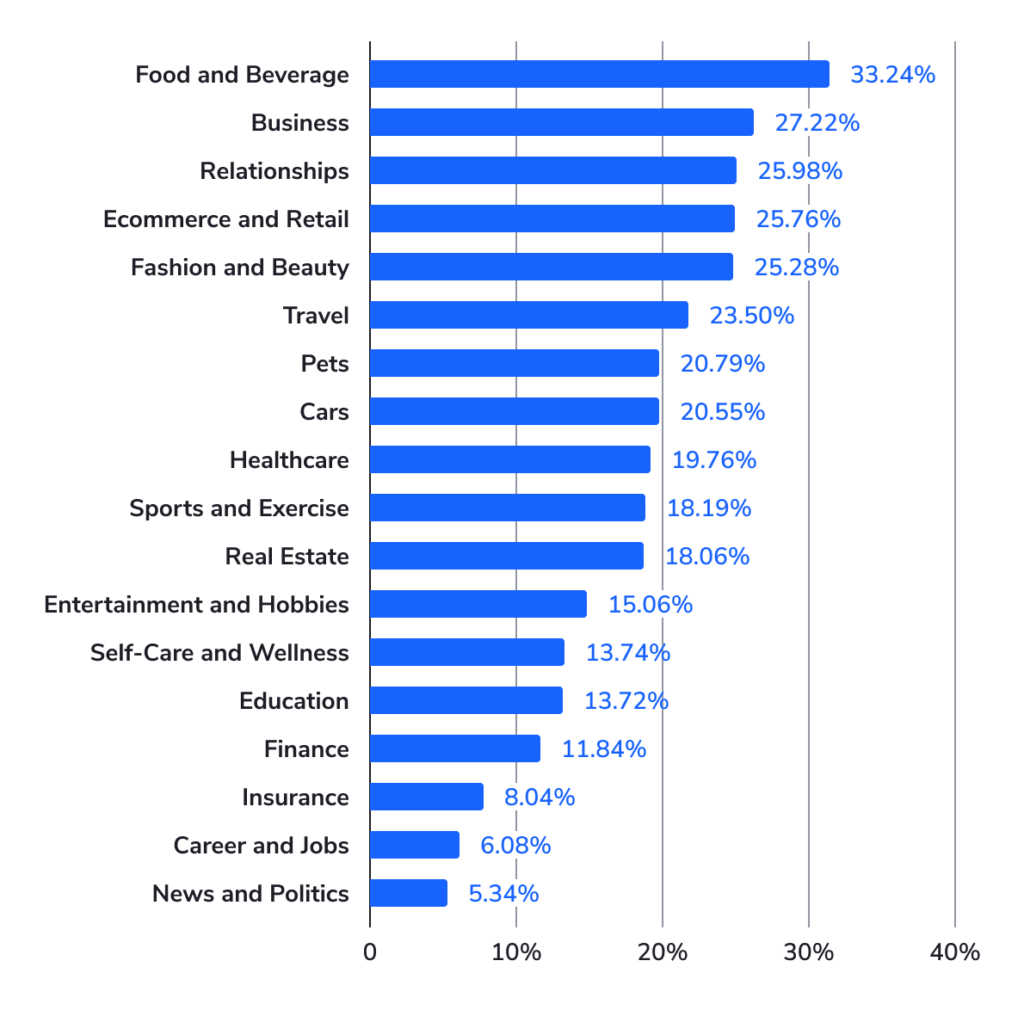
My Take: Yevheniia conducted the most recent and comprehensive research to date. She analyzes everything from vertical coverage to ad placement and frequency around SGE. One of the risks around the sources of SGE that she reveals is the overwhelming reliance of forums like Quora and Reddit for results. Considering that much of this content is unvetted experiences from anonymous users, it’s surprising that Google would allow SGE to frequently intermingle it with the Generative output.
When searching for the best movies of all time, SGE told me that a Reddit user thinks Godfather is the best movie. That’s great. Thanks, SGE.
All of these research reports show that SGE is impactful, inevitable, and will require a reframing of how SEOs strategize.
What do SEOs need to consider as SGE appears among the keywords they’re targeting?
What is AI Overviews' impact on SEO?
With Google releasing AI Overviews publicly. Time is of the essence. SEOs need to consider how AI Overviews might steal traffic from their content and what they can do to proactively mitigate that outcome.
Assuming that AI Overviews appears on your keyword, the biggest question remains whether searchers will interact with it. If they do, will it serve as a novelty that they’ll eventually become cognitively blind towards or will it become the primary way they engage with search?
In their first test, users didn’t appreciate the AI Overview interrupting their search.
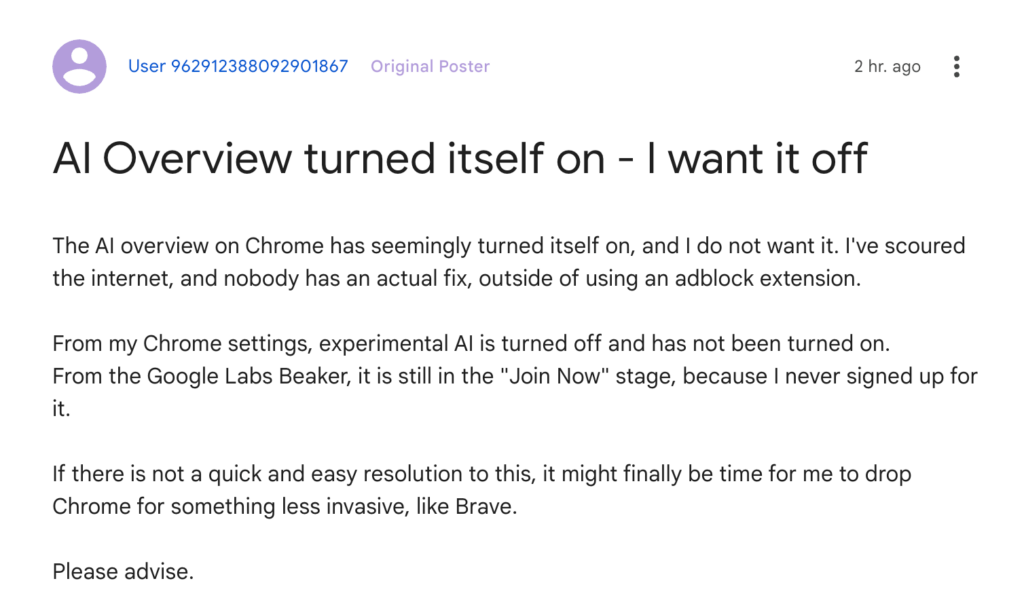
Most likely, it will depend on your audience. For a simple query, it will eventually serve as a stronger satisfier of search intent than the featured snippet.
For more complex queries, searchers will most likely continue on to websites to either conduct more research about products and services or to find more personalized expertise and experienced contextual information that they trust.
Trust is a big factor.
Right now, for most queries: AI Overviews are not a better alternative to intuitive human research.
How quickly will that change?
Assuming that searchers lock into AI Overviews, then your brand needs to appear in the generative output for visibility and remain top of mind.
Different types of queries will have different levels of risk. Aleyda Solis hypothesizes that there are 3 SGE risk levels to consider:
- Low risk: When SGE duplicates what’s already in the SERPs (some Local Map Packs).
- Low-Medium risk: When SGE summarizes an article, but still provides a clear link to it.
- Medium-High risk: eCommerce affiliate publishers that might lose traffic to product selections in the result.
Additionally, there are major considerations for brand reputation. Traditionally, a result for a brand would have organic links that a PR team could help mitigate. We have much less control over the AI Overviews output. If anything, that would give you a quick glance at your brand’s sentiment.
For different industries beyond eCommerce, there are other considerations:
- Google continues to threaten the travel industry with AI Overviews tips ripped from bloggers and now AI itineraries are being included in results.
- The News Industry has the threat of pulling hard-earned journalistic sources from their content and into AI Overviews. They can’t really afford to block Googlebot from using their content if they depend on organic search for traffic as their primary business model. I wrote about what News Organizations can do to prepare for AI Overviews.
- We’ll keep our eyes on the backlash for AI Overviews output for YMYL searches. All it takes is a few consequential results and Google might significantly roll back on the types of queries that trigger AI Overviews.
Regardless of how you feel about AI Overviews. It’s coming. The best thing you can do right now is proactively get in front of it as best you can. Besides, businesses should have a holistic, multi-channel marketing strategy in place.
In the meantime, for a step-by-step guide on how you can begin your own experimentation with optimization for AI Overviews, check out my article.
For additional quick-hit tactics, read Malte Landwehr’s recommendations on LinkedIn.
Watch the replay of our FREE webinar on AI Overviews Optimization and get a head start on your AI Overviews prep.
A final consideration for SEOs trying to wrangle AI Overviews. At this point, there’s no reporting on traffic from AI Overviews. We don’t have anything appearing in Google Search Console (like we do for Google Discover). It’s unknown if we would see that type of reporting in a reasonable amount of time. While Google has invested more resources into Google Search Console recently, it hasn’t always been historically dependable.
Besides, if AI Overviews does get adopted by searchers, it’s likely to evolve how we search. Instead of shorter and simpler searches, people will start to get more nuanced in their searches. It’s data that will be hard to do much with at scale.
The Future of AI Overviews and SEO
AI Overviews has the potential to completely disrupt the way that everyday users actually search. At this point, I ignore it unless I’m performing SEO research. I find myself glossing over the click to generate button or the truncated click to expand button on desktop and mobile.
And that’s not to say that the normal search results are always satisfying. They’re just better than AI Overviews results.
It still takes work most of the time to get to the answers and information we need unless it’s painfully obvious. And I make a living in Search.
The dream future scenario of search is that Google can more effectively pick up context and deliver exactly the concise, key pieces of information in the right format (text, images, video, data), that we’re searching for. I’d gladly trade certain segments of my data for a personalized experience on Google. If you can use my searches, device usage, and location to provide a perfect search experience, go for it! (I might be in the minority, but what other choice do we have for a better search experience?)
The Impact of AI Overviews' Novelty
So the question remains whether AI Overviews will be a pure novelty for the average person. Will your grandma, daughter, emo punk friend from high school, or local small business owner use it?
Unless they’re forced to deal with and forced to use it, they might be opposed. Humans hate change. We love the status quo. And many of us are not likely to work hard to make our situations easier. How many people read the directions? Oh. Most people? Depends on what we’re putting together or using, right?
Brands Need to Be Prepared
There are two major considerations for brands for AI Overviews.
- Does your content and links to your website appear in AI Overviews?
- Do you get mentioned in AI Overviews because of your Brand and Authority in your space?
Industry leaders have a baked-in advantage. If you’re already considered the top brand among competitors and have been for a period of time, all of the training data will be biased toward your brand. New fresh info that’s included via RAG will influence the SERPs, but you’ll have less difficulty entering new searches.
Digital PR will continue to be a core part of your holistic SEO strategy. Whether we call it ‘Barnacle SEO’ or ‘Surround Sound SEO’ doesn’t matter. Appearing in best-of lists, partnerships, social media– will all drive visibility in AI Overviews beyond pure relevance to the searches.
Will Content Creation and Publishing Change?
If we see AI Overviews siphoning off organic search traffic in greater amounts, will we see a smaller investment in original content? There’s a legitimate risk for smaller publishers to be unable to monetize their content if traffic dwindles. That might impact strategy and the number of competitors in a given field. Independent of AI Overviews, we’re seeing Google’s recent Helpful Content System, Spam Update, and Core update decimate affiliate content sites and many niche bloggers. There are a tremendous amount of false positives, but the impact has been pretty loud in the SEO community.
Will that reduce a generation of content creators? If the focus moves to different social media platforms, you might see a different format of search where Google starts to incorporate content from those channels in the same way that it depends more on Reddit and Quora. I wrote about Reddit and Google and their recent partnership.
Google needs to find ways to support content creators, media publishers, and the like. Unless they have a plan in place, this whole movement is a risk to their ad revenue model.
Our Roles as SEOs in an AI Overviews Future
While developing a stronger presence among marketing teams, SEO still doesn’t have the seat at the table that Advertising professionals do. Like Millennials in the generation wars, SEOs risk Social Media marketing stealing their seat at the table. However, that analogy probably won’t bear fruit. SEO is changing.
Adapting will require a reframing of content production for search that works within the value that AI Overviews will deliver. We still need to appear across the entire buyer’s journey, but we’ll most likely need to:
- Focus more on the bottom of the funnel. Be discoverable where people are more likely to make a buying decision.
- Use structured data and unique information (information gain) to stand out. Original ideas and proprietary information will be the USP.
- Invest heavily in brand building. Google will continue to connect the real world and the online world. Perception and visibility are becoming more tied to Brand every day.
- Do it all with less reporting. We don’t know if AI Overviews will provide attributable reporting in Google Search Console. People will start searching with longer, more context-dependent, and nuanced queries. We want scale and volume, but we’ll need to effectively report on topics, categories, and subcategories in place of individual keywords.
What do think the future holds for search, AI Overviews, and SEO?
Next Steps
Here are three ways iPullRank can help you combine SEO and content to earn visibility for your business and drive revenue:
- Schedule a 30-Minute Strategy Session: Share your biggest SEO and content challenges so we can put together a custom discovery deck after looking through your digital presence. No one-size-fits-all solutions, only tailored advice to grow your business. Schedule your consultation session now.
- Get Our Newsletter: AI is reshaping search. The Rank Report gives you signal through the noise, so your brand doesn’t just keep up, it leads. Subscribe to the Rank Report.
- Enhance Your Content’s Relevance with Relevance Doctor: Not sure if your content is mathematically relevant? Use Relevance Doctor to test and improve your content’s relevancy, ensuring it ranks for your targeted keywords. Test your content relevance today.
Want more? Visit our blog for access to past webinars, exclusive guides, and insightful blogs crafted by our team of experts.







