“The funnel as we know it is moving,” says Christian Ward, Executive VP and Chief Data Officer at Yext. Thanks to AI, it’s moving off your website and into a chatbox (or in various forum discussions online), and marketers in the local business space need to pay attention.
It’s vital to ensure that the right people find your business wherever they’re searching without having to filter through too many irrelevant results. Like with Relevance Engineering, your brand strategy must be omnimedia and span social media, YouTube, Reddit, and other places.
Although some studies point out that Google is still the top source for search right now, there’s a lot more nuance to that.
“That’s like measuring a baseball player by the number of swings at bat,” Christian said. “That’s not how you measure search. Search has to be around the time you spend on a platform because that’s where the money is made, and it’s got to be measured on outcomes.”
And while AI outcomes aren’t that great yet, they are slowly getting better.
Yext performed a citation study on 6.9M citations, asking 1.6M questions across three models (ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity) to find the impacts of AI Search on local visibility. This article will go through the data and findings.
The Impact of Search Fragmentation
Search is fragmenting. People are starting their searches on LLMs, Reddit, TikTok, and other places, and often moving to Google later on in the process to fact-check or make a final purchase. AI Search is decentralizing the search process.
Christian created the below chart two years ago. It’s evolved, yet still highlights how people use a wide range of platforms to search, but Google still dominates the market and sits in the middle (especially for fact checking).
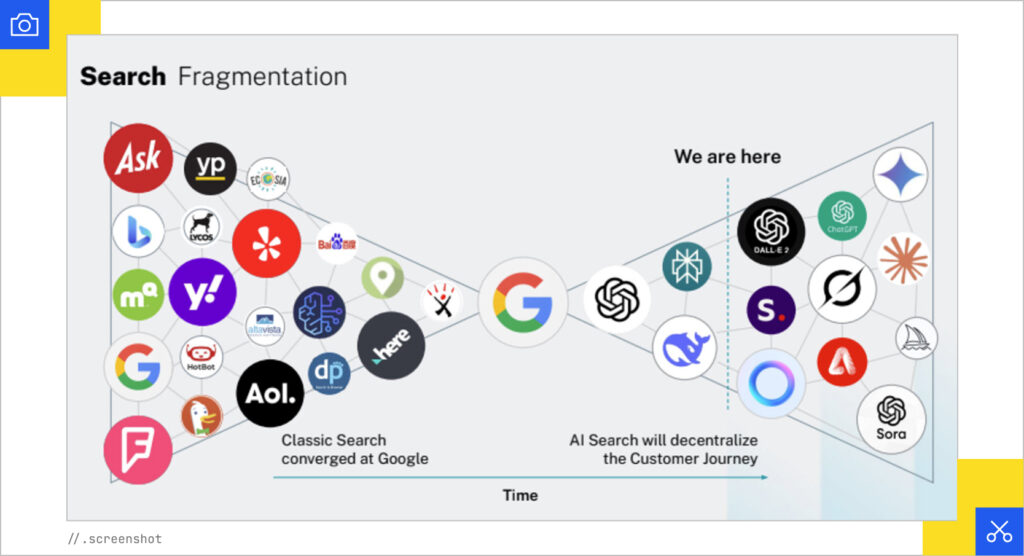
Even if TikTok is your first stop for research, eventually the platform will add an LLM of its own. And while users are starting exploration in AI but going to Google to execute, that won’t last so we need to be prepared.
“That’s gonna stop really soon as AI models add more executions,” Christian said.
The Growth of AI
In just 2 years, ChatGPT acquired as many users as the entire internet did in 13 years.
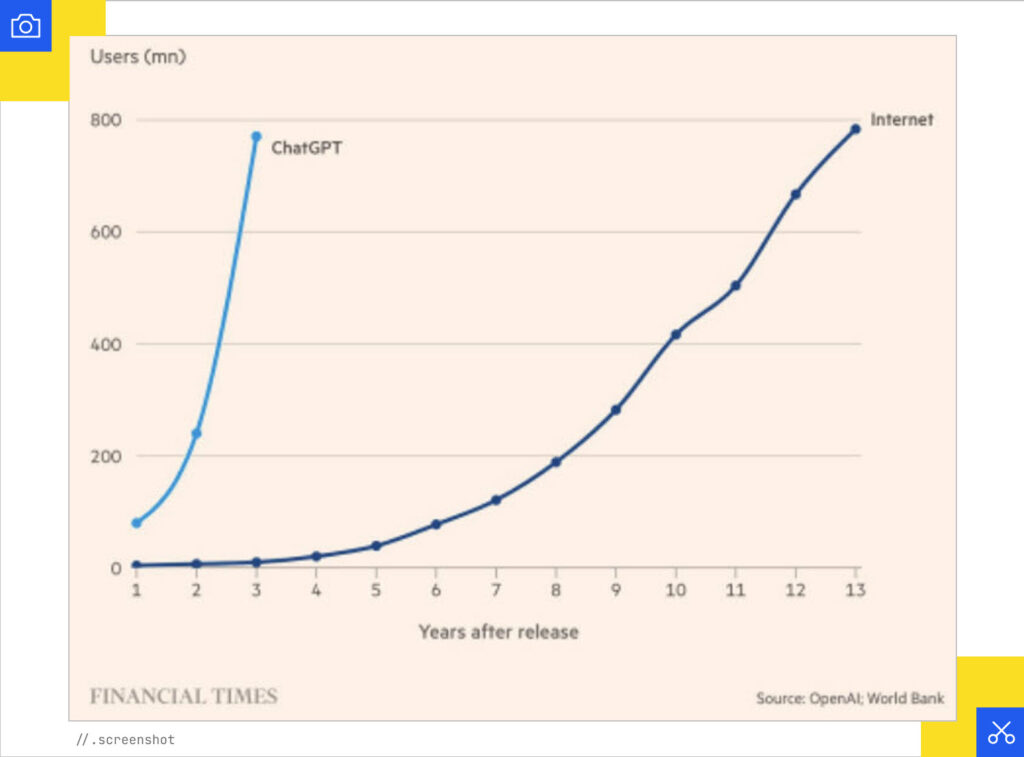
Unlike with old-school dial-up internet, when no one in the house could use the phone while you were online, there’s no cognitive burden to AI. You can just use it easily.
And with the creation of AI Mode and constant improvements to Gemini with each release, Google will clearly be focusing its attention on AI.
“I don’t see Google just continuing to do search,” said Christian.
As search continues to fragment and more partnerships pop up with AI companies, we’ll see changes in how we measure success. Direct purchases within LLMs will impact traffic and clicks.
Walmart’s deal with ChatGPT for in-app purchases contributes 20% of Walmart’s referral traffic. This partnership with OpenAI means that Walmart can’t capture all the metrics that it used to, but at this point, they don’t even care. They just want the customer to check out, regardless of whether it’s on Walmart’s site or in ChatGPT.
In fact, traffic to many sites is down, but many businesses are still getting relevant clicks because visitors to their sites likely did extensive research before arriving.
“If they play their cards right in how they are cited and the knowledge they provide, I think they’re going to have phenomenal business outcomes,” Christian said.
However, this brings up another question. Should sites develop two types of content: one for machines and one for people? Or is a combination of the two the way to go?
“There are so many strategic applications for that for business,” said Garrett Sussman, Director of Marketing at iPullRank.
There’s a lot of data we still need to see to truly understand all of AI’s impacts on search fragmentation, but that probably won’t happen, and Christian says we need to just get used to that. There will be discomfort around monitoring, strategy, and search behavior as AI Search becomes a more integrated part of the way we search. We’re not going to get all of the data that helps us determine resource allocation and return on investment.
But some changes will have a more positive impact, like improvements to memory and personalization in LLMs. Memory will be the step that solidifies where and how we search.
The Evolution of Memory
Memory and personalization will be a huge part of the future development of AI systems, according to Sam Altman of OpenAI who has said that ChatGPT-6 will be all about improving its memory.
The main issue for Google and OpenAI is that with more memory in search, there is an impact on ads and a company’s ability to show you valuable ads at the right stage in the search journey. Memory context and location will have a huge impact on how different the search results are for everyone.
“The reality is, if I can’t have the right to show you steak restaurants because you’re a vegan, that’s a problem for the available ad space,” Christian said.
Memory in AI shrinks the ad reach because there’s only a limited number of products or services that make sense. You can’t deliver broad ads because people will stop asking broad questions. At the same time, it increases the value of the ad itself because you’re further down the funnel to your target.
“It’s a better user experience for us,” Garrett added.
But how does this play out next year?
Every so often throughout the evolution of computer technology, we’ve seen inventions jump from compute to memory improvements, and OpenAI is heading toward a memory jump.

If ChatGPT can master memory, it will have a huge advantage in the market.
“If it starts getting to that level, I think you will see a very big upswing in the value proposition to the consumer,” Christian said.
The Impact of Experience Fragmentation
An AI company’s greatest risk is users not trusting them because they can switch to another LLM so easily. If you ask one of the AI models a question, and it answers it wrong, you will probably go use another model. Google’s built up brand trust over decades. They have more at stake to get it right. AI introduces a complex risk to that trust due to the probabilistic nature of generative output.
For users, there is no cognitive burden when using LLMs for search. You don’t have to learn a whole new system because they’re all pretty much the same and very easy to operate.
There’s not going to be a one-size-fits-all solution to this, but accurate citations will have an impact. And how you format your content will control your chances of being cited.
“I think AI has a trust problem,” Christian said. “If trust is the currency by which AI will be judged and scored, then citations are the receipts.”
Citations. That’s why Christian is obsessed with where they fit in the puzzle. They are critical to the LLM-to-internet ecosystem.
Citations are dependent upon: the [QUESTION], the [CONTEXT], the [LOCATION], and the [MODEL].

The above example of a query shows the various ways people can find your business due to how your company is talked about online.
- Subjective qualifiers like “best” typically come from review sites.
- Categories like “Indian restaurant” come from listings and directories.
- Locations like “Soho” come from maps and local pages.
- Objective facts like “late night dining” or “patio seating” come from websites and pages.
“Every element on this page has a different level of potential verification by a probabilistic large language model,” Christian said.
If a fact is shown only on your site and nowhere else, that makes it seem less trustworthy in the eyes of AI. But if it also appears in reviews or on other sites, the higher the probability that your business will show up in an answer.
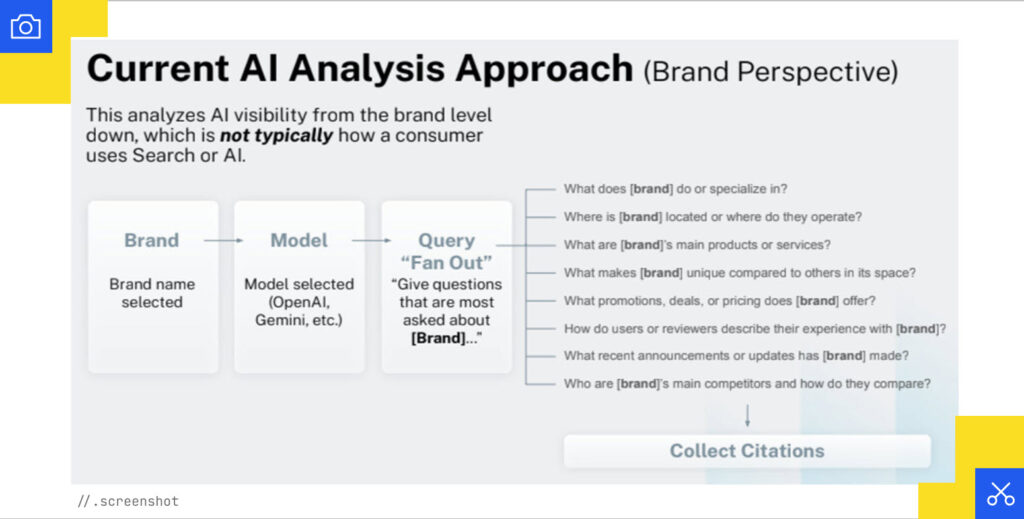
AI typically utilizes location, context, and memory during a search. Currently, we analyze AI visibility from the brand level down, which is not typically how a consumer uses search or AI.
Christian posits that AI Search results heavily depend on location. Every search is impacted by location in some way.
A Starbucks in the suburbs of Georgia will see different business than one located in midtown Manhattan. If you own a burger restaurant in a small town, your competition likely isn’t tons of other burger joints but rather the two or three other restaurants in town.
Mentions also have an impact here. Along with structured data, these are important to the customer journey. Common page structures, such as neighborhood, region, state, city, or any geography, need a dedicated page on your site.
Christian emphasized that we need to stop thinking globally about brand and focus instead on the consumer’s perspective regarding what’s showing up and being cited. If you’re a plumber, odds are that you want more leads for bathroom remodels than 2 a.m. calls for a clogged toilet, so your content needs to reflect that in order to be properly cited.
There are some factors you can control and that is where you should focus your marketing efforts.
What Can You Control?
Understanding that local AI Searches are probabilistic, but location has an overwhelming impact, the sphere of influence is physically reduced significantly. But of those potential citations, what can you actually influence?
A number of citation source control categories can impact visibility:
- Websites
- Listings
- Reviews and social
- News and forums

You can’t really control what people say in reviews or on social media and forums such as Reddit, so Christian says you shouldn’t spend all your time worrying about those. In fact, he describes the current environment as “an existential threat” for review sites. You can see reviews of products anywhere now, from TikTok and Instagram to Reddit, so there’s no need for people to go to specific review sites anymore.
You can control what’s depicted on websites, third-party directories, and local websites.
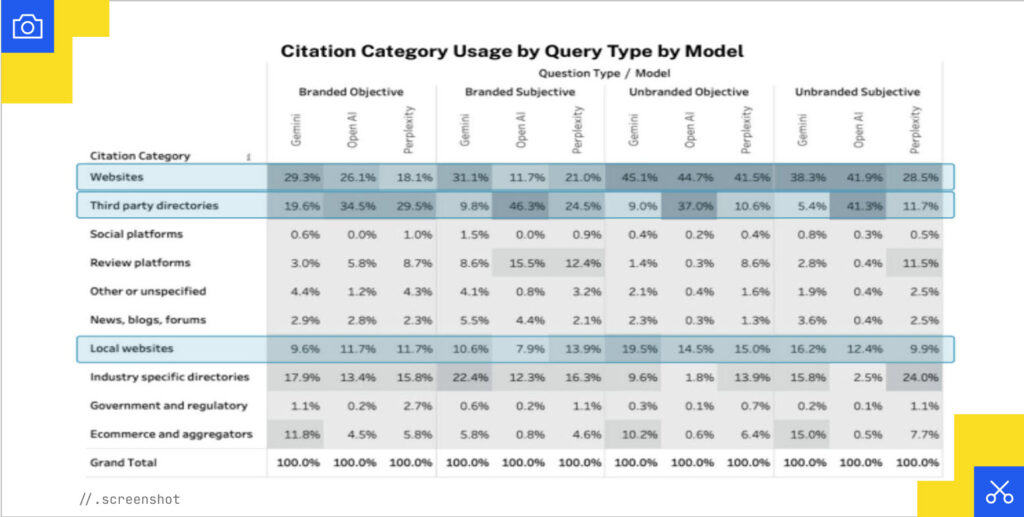
Local websites with subdomains are a large percentage of what’s cited because AI doesn’t have to compute all the folder structures. There’s just a concise and specific page from which to gather information.
And although Google doesn’t specifically cite Google Business Profiles, that doesn’t mean it’s not a source of data; they simply don’t cite it. You should still make sure your profile is updated and accurate.
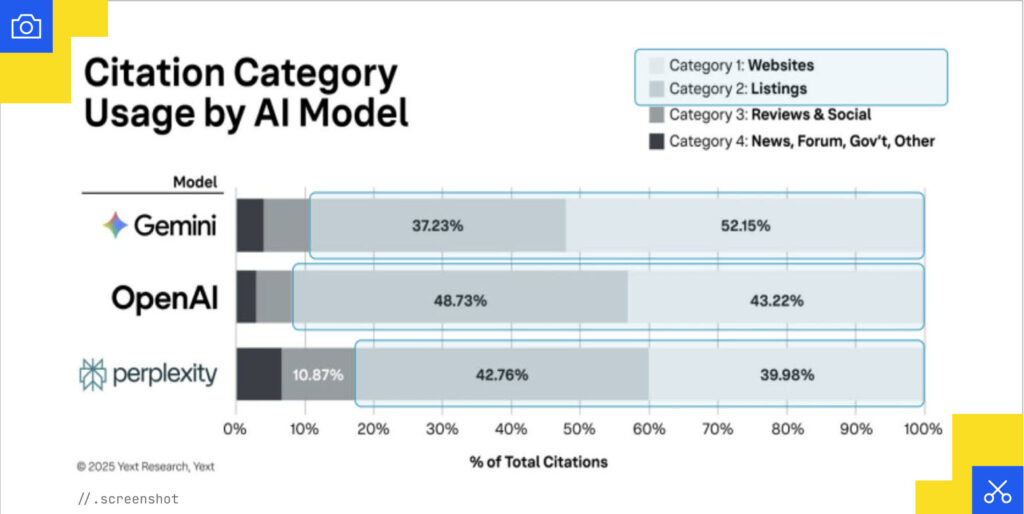
According to Yext’s data, OpenAI, Perplexity, and Gemini are not far apart when it comes to the percentage of total citations for each citation category. And for the most controllable sources, websites and listings, citations show up very often in those models. This means there is a lot of opportunity for local businesses to control how they’re cited and found by prospective customers.
Local Search Takeaways
Location is everything. The data from Yext shows that websites are leading the citation race and that lead is expanding. Online profiles and directories also serve as crucial verification points for AI models, reinforcing what you’re saying about your business across the web.
Interestingly, Yext has seen social and review citations decline from where they were just three months ago. This shift means the controllable sources (your website, listings, and structured data) matter even more than they did before. The power is back in your hands to shape how AI models understand and cite your business.
It’s all about omnimedia strategy these days. The LLMs will pick up information about your brand from all different sources such as YouTube comments, Reddit forums, TikTok reviews, etc. You need Relevance Engineering to make sure your brand is showing up in a positive way everywhere people search.
While many sites are scrambling to block crawlers because they’re worried about giving away their content, that’s the wrong move. If you block AI from accessing your information, you’re essentially removing yourself from the conversation happening in these models and opting out of future search visibility. Your local business needs to make it easy for AI to find, understand, and cite it accurately, or you’ll be left behind.






