“The general idea is we’ve moved from, ‘Do we rank?’ to, ‘Are we cited?’” said Zach Chahalis, Senior Director of SEO and Data Analytics at iPullRank. “The metrics that we need to care about, though, have changed.”
To begin understanding what we need to track in this new age of AI search, there are four questions marketers should be asking themselves:
- Are we cited?
- Is traffic coming in?
- What are visitors doing on our site?
- Are they converting?
The answers to these questions come from new metrics that you should be tracking so you can properly gauge your site’s success.
The evolution from traditional search to AI-powered discovery is changing how we think about visibility, so it requires a completely new approach to measurement. This blog will look at some of the new metrics and how they can help your business.
Where AI Factors Into Search
Before we jump right to the metrics, we need to do a quick recap on how AI search works. AI search is a change from deterministic rankings, where content is surfaced largely as-is based on predefined scoring signals, to probabilistic rankings driven by large language models that interpret, synthesize, and reason across multiple sources.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is the core pattern behind AI search and powered by hybrid retrieval (which is a combination of both lexical and semantic search, reranking documents using reciprocal rank fusion).
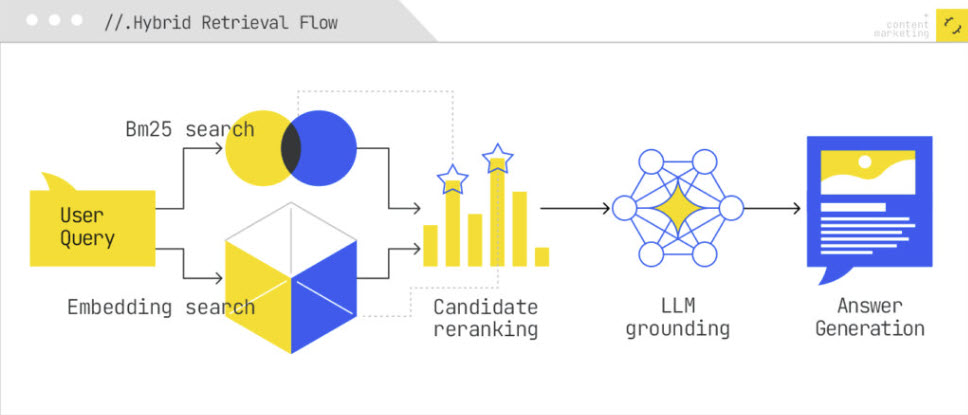
Semantic understanding is driven by vector representations of meaning. Everything gets embedded in the same space, which means AI search indexing is inherently multimodal.
“You need to ensure that your content performs well in those modern retrieval systems by structuring it in a way that’s both machine-readable but also human-friendly,” Zach said.

Go too machine-readable, and people won’t stay on your site. It’s a balance you must meet (and iPullRank’s Relevance Doctor tool can help with this).
How to Optimize for AI Search
There are a few methods you can use to optimize your content for visibility in LLMs. These include:
- Structure your content into semantic chunks that are optimized for extractability. In other words, short, easily defined sections with clear headings and subheadings that answer specific questions directly.
- Use entity-rich, embedding-friendly language with clearly defined entities, consistent terminology, and modifiers and descriptors (qualifiers like size, function, location, and purpose help differentiate similar entities).

- Monitor bot activity via log files to analyze how AI crawlers are viewing your website, and monitor for crawling issues and inefficient use of crawl and render budget.

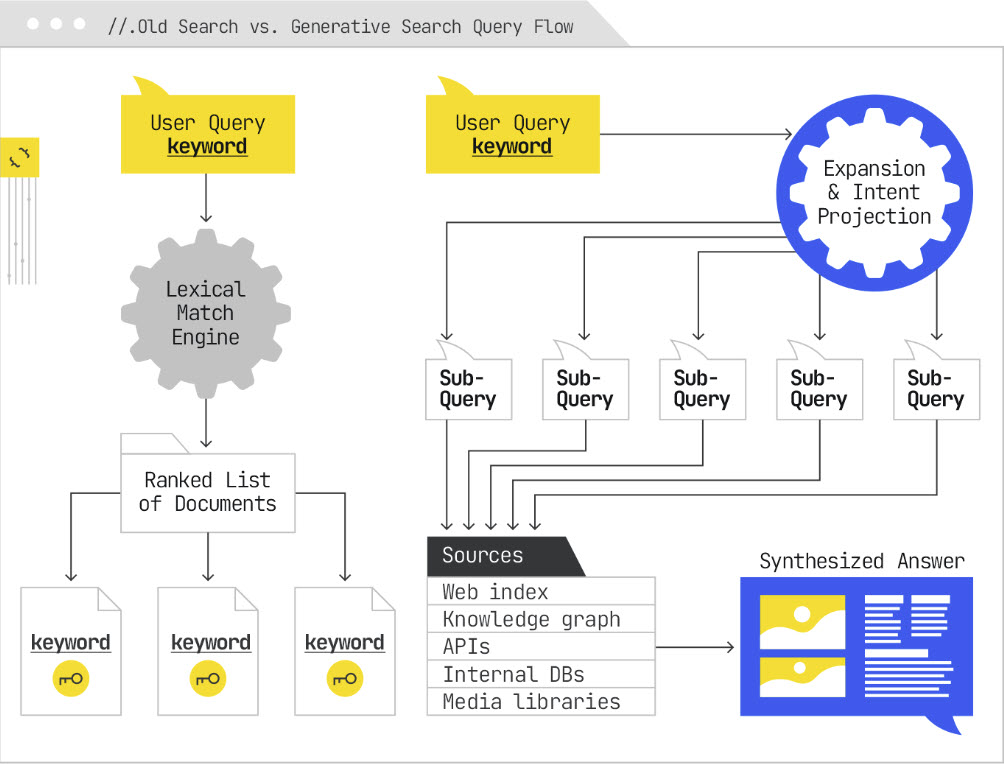
- Understand query fan-out and how it can gather passages from multiple sources for a more complete answer.
“This takes the original search and then looks into dozens of related personalized and contextual variations, all behind the scenes, before that response even generates and comes back to you,” Zach said (and iPullRank’s Qforia tool can help identify fan-out queries).
The New Metrics of Success
With the advent of AI search and its negative impact on website traffic, marketers need to rethink how they measure success and report it to executives.
Here are the new metrics to consider:
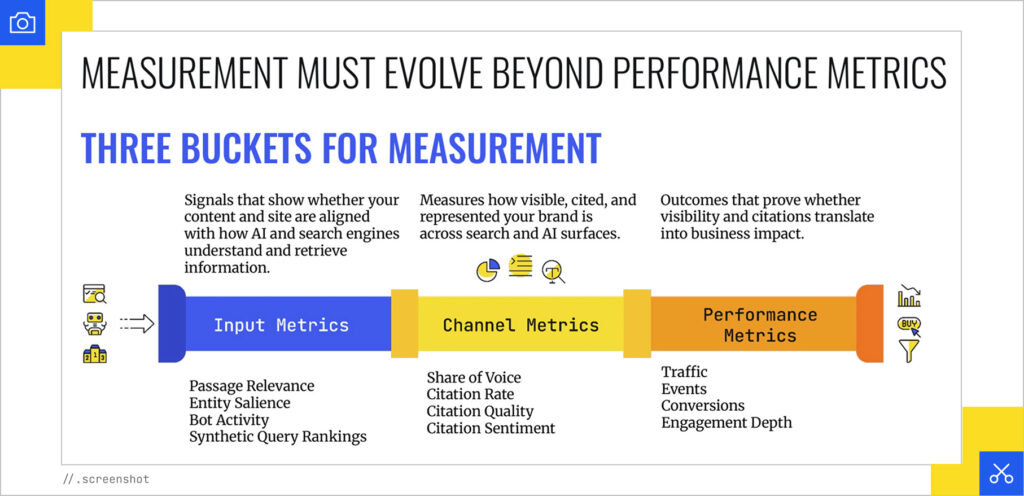
Input Metrics
These are the signals that show whether your content and site are aligned with how AI and search engines understand and retrieve information.
Think of these as your foundation:
- Passage Relevance – How well your content chunks perform in retrieval systems
- Entity Salience – How clearly defined and rich your entities are
- Bot Activity – What AI crawlers are actually doing on your site
- Synthetic Query Rankings – How you perform across query variations
Channel Metrics
These measure how visible, cited, and represented your brand is across search and AI surfaces.
“In order to be considered for AI search, you need to be considered high quality, and your citations need to be accurate, verifiable, and point to authoritative sources.”
- Zach Chahalis
- Share of Voice – Your competitive visibility in the space
- Citation Rate – How frequently AI search engines cite your site
- Citation Quality – Whether your citations are accurate, verifiable, and authoritative
- Citation Sentiment – Are citations about your brand positive or negative?
You should be looking at all of these factors and using them to inform your content strategy. Uplevel your content to align with citation quality. If your brand has negative mentions, create content in response.
At iPullRank, we call it “10x-ing content,” or creating content that’s 10 times better than what’s out there in order to be competitive.
“If you are being seen in a negative way, there’s potential the AI platforms are less likely to talk about your brand,” Zach said.
There’s a difference between citations and mentions, however. Tracking mentions is more complicated, but you should still try to track them wherever possible because the more your brand is talked about, the better you’ll perform in these channels.
“Brand mentions are kind of the new currency of AI search between how good your content is and how much you’re answering questions that folks are looking for.”
- Zach Chahalis
You can try tracking Google Alerts to see if your brand is being talked about and how.
Ray Grieselhuber, CEO of DemandSphere, recommends a DIY method:
“Build up your own internal mapping of all the different properties that are relevant to your brand and treat those as candidates for potential mention tracking,” he said.
Performance Metrics
These are the outcomes that prove whether visibility and citations translate into actual business impact:
- Traffic – Sessions coming from AI search and LLMs
- Events – Meaningful user actions on your site
- Conversions – The bottom-line results
- Engagement Depth – How users interact with your content
Be sure to measure your referral data. Ensure that you monitor sessions, conversions and revenue coming from AI search/LLMs in your analytics instance (by using GA4/Adobe/Amplitude/Etc.). Also, closely monitor your URL/Page-level data to identify additional insights and aid your optimization strategy.

Create a custom channel grouping as well. LLM traffic comes in as a referral channel in GA4, but GA4 is also well known for incorrectly classifying other sources of traffic. Consider creating a custom channel grouping to properly classify all sources, and then set a specific channel grouping for LLMs.

Measure engagement metrics, which factor into traditional search extensively via NavBoost, which can impact AI search through RAG. Track everything from time on site to conversions. Simply put, provide a good experience for your users and you’ll get good results.
You should also understand how traffic becomes revenue. It is vital to understand data points such as average order value or the value of a lead for your business. This helps your business effectively develop a return on investment metric on your AI and organic traffic.

The Future of Metrics in AI Search
Many organizations are still measuring success using yesterday’s metrics. They’re tracking keyword rankings and SERP positions, while the future of metrics has moved to something entirely different.
This is why the three-tier metrics framework matters so much: understand and monitor your input metrics, channel metrics, and performance metrics.
Start with the basics: get your log file analysis set up, create those custom channel groupings in GA4, begin scoring your passages for relevance and mapping your entities, track your citations, and understand the sentiment around your brand. Connect all of this to revenue so you can prove the value.
Your existing content strategy, technical SEO foundation, and analytics infrastructure all still matter. You’re just adding new layers of measurement and optimization on top of what already works.
And if you need help, we’re right here to support you.
“If you can’t answer those questions because you don’t have those data points, that’s where I highly recommend talking with an expert in the data analysis space,” Zach said. “Being able to know what that value is to you is vital.”
And check out the other 2 articles in this series based on our webinars with Sitebulb:






